Energy Storage: The Foundation of Grid Flexibility
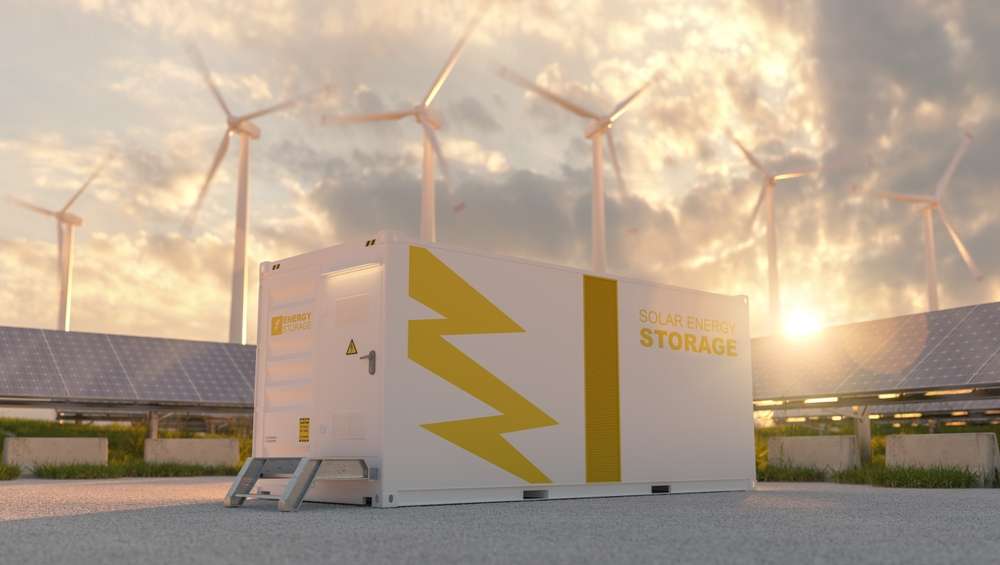
Battery energy storage systems are increasingly vital in modern energy infrastructure, ensuring system stability and efficiency. With the growing integration of renewable sources like solar and wind power, the ability to store surplus energy becomes critical for balancing supply and demand, as well as enhancing the reliability of electricity grids worldwide, including in the United Kingdom.

Applications of Battery Energy Storage in Modern Grids
Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) are a cornerstone for modernising electricity grids. They facilitate the integration of diverse energy sources, encompassing both traditional and renewable options, thereby ensuring flexibility and stability. These systems are capable of rapid responses to fluctuations in energy consumption, providing crucial services such as frequency regulation, voltage support, and peak load management. Storing energy during periods of low demand and releasing it during high demand helps optimise the utilisation of energy resources and reduces the necessity for constructing additional generation capacity across local services and broader grids.
Types of Batteries for Energy Storage and Their Efficiency
Several primary types of batteries are employed for large-scale energy storage, each possessing distinct characteristics. Lithium-ion batteries are widely adopted due to their high energy density, extended cycle life, and relatively fast charging capabilities. However, flow batteries are also utilised, offering significant scalability and a long operational lifespan, although their overall efficiency might be slightly lower. Lead-acid batteries, despite having a lower energy density, remain an economically viable solution for specific applications. The selection of battery technology is contingent upon the system’s specific requirements regarding capacity, power output, and desired service life, impacting the overall efficiency of the storage system.
Integrating Renewable Power Sources and Grid Management
Energy storage plays a central role in the effective integration of renewable power sources, such as solar and wind farms, which are inherently intermittent. Battery systems enable the smoothing of energy production fluctuations by storing surpluses when solar generation is high or wind speeds are favourable, and then discharging this energy into the grid when production declines. This ensures a more reliable and stable supply of electricity and reduces reliance on conventional power sources. Through robust grid management strategies utilising BESS, energy flows can be optimised, losses minimised, and the overall resilience of the energy system enhanced, benefiting consumers in your area and beyond.
The Future of Energy Storage Technology and Innovation
The future of energy systems is significantly dependent on the continued advancement of energy storage technologies. Innovations in materials science and battery chemistry promise increased capacity, reduced costs, and enhanced safety. Research efforts are focused on developing novel battery types, such as solid-state batteries, or improving existing solutions to achieve even greater efficiency and durability. The expansion of energy storage capacity and its integration with Smart Grids unlock new possibilities for decentralised energy generation and improved resilience against external disruptions, contributing to global and local sustainability goals through technological innovation.
| Product/Service | Provider/Type | Cost Estimation (GBP per kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Home Storage Systems | General Solutions | £400 – £1200 |
| Commercial Systems | Industrial Solutions | £240 – £640 |
| Large-scale Grid Systems | Utility Solutions | £160 – £400 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Economic Considerations and Cost of Energy Storage Solutions
The cost of energy storage systems is a critical factor for their widespread adoption. In recent years, prices for lithium-ion batteries have significantly decreased, making them more accessible for various applications, from residential installations to large-scale grid solutions. The total system cost encompasses not only the batteries themselves but also inverters, Battery Management Systems (BMS), installation, and operational expenses. While initial investments can be substantial, long-term savings from optimising energy consumption, reducing peak demand charges, and participating in grid services can yield a significant return on investment. Ongoing technological development and increased manufacturing volumes continue to drive down costs, making these solutions more viable for a wider range of users.
Energy storage systems are an integral component of modern energy infrastructure, providing flexibility, stability, and efficiency. Their role in grid balancing, integrating renewable sources, and supporting sustainable energy supply will only continue to grow. Persistent innovation and decreasing costs make these technologies more accessible, paving the way for a more reliable and environmentally friendly energy future.