Imaging Techniques for Detecting Cerebral Masses
Detecting cerebral masses, often indicative of conditions like brain tumors, is a critical step in neurological care. Advances in medical imaging have transformed the ability of healthcare professionals to visualize the intricate structures of the brain, identify abnormal growths, and plan appropriate interventions. Understanding the various imaging techniques available provides insight into how these conditions are diagnosed and managed, offering a clearer picture for both patients and their families.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
Understanding Cerebral Lesions and Growth
Cerebral lesions refer to any abnormal tissue in the brain, which can range from benign conditions to malignant tumors. The identification and characterization of these growths are paramount for effective patient care and treatment planning. Malignant brain tumors, often categorized under oncology, represent a significant health challenge, requiring precise diagnosis. Early detection of these lesions and understanding their growth patterns are crucial for improving prognosis and guiding therapy decisions. Medical research continuously seeks more accurate and less invasive methods for detecting these cranial abnormalities.
The Role of Imaging in Diagnosis and Prognosis
Imaging plays an indispensable role in the diagnosis of brain tumors and other cerebral masses. It allows neurologists and oncologists to visualize the size, location, and characteristics of a lesion without invasive procedures. This diagnostic capability is fundamental for determining the type of growth, assessing its potential impact on brain function, and establishing a prognosis. Beyond initial diagnosis, imaging techniques are also vital for monitoring the effectiveness of treatment, detecting recurrence, and guiding neurosurgery. The detailed insights provided by various imaging modalities help tailor individualized treatment strategies.
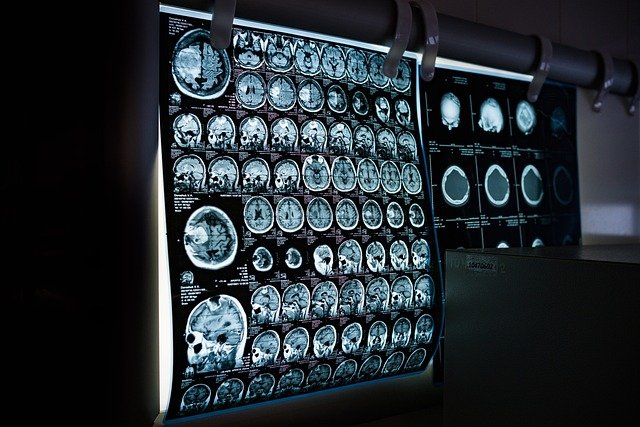
Common Imaging Modalities for Brain Tumors
Several imaging techniques are routinely employed to detect and characterize brain tumors. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is often considered the gold standard due to its superior soft tissue contrast, providing detailed images of the brain structure and any abnormal tissue. Computed Tomography (CT) scans are faster and widely available, often used in emergency situations or when MRI is contraindicated. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, particularly with specific tracers, can reveal metabolic activity within tumors, differentiating active growth from scar tissue. Each modality offers unique advantages in the comprehensive assessment of cerebral health.
Advanced Imaging Techniques in Neurology and Neurosurgery
Beyond standard MRI and CT, advanced imaging techniques provide even greater detail and functional information crucial for complex cases. Functional MRI (fMRI) measures brain activity by detecting changes in blood flow, which is invaluable for mapping critical brain functions before neurosurgery to minimize damage. Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (MRS) can analyze the chemical composition of brain tissue, helping to distinguish between different types of tumors or between tumor and non-tumor tissue. Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) visualizes white matter tracts, aiding surgeons in planning approaches that preserve vital neural pathways. These advanced tools enhance diagnostic precision and support intricate surgical interventions.
Patient Care and Treatment Planning
Effective patient care for individuals with cerebral masses involves a multidisciplinary approach, integrating diagnosis, therapy, and ongoing management. Once a cerebral mass is detected through imaging, a team of specialists, including neurologists, neurosurgeons, oncologists, and radiation oncologists, collaborates to devise a personalized treatment plan. This plan might include surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination of these. Imaging continues to be instrumental throughout the treatment journey, from pre-surgical planning to post-treatment follow-up, ensuring that interventions are as effective and targeted as possible to improve patient outcomes.
Imaging techniques are central to detecting and managing cerebral masses, including brain tumors. The costs associated with these procedures can vary significantly based on factors such as the specific imaging modality, the geographical location, the healthcare provider, and whether the procedure is performed on an inpatient or outpatient basis. For instance, a standard CT scan is generally less expensive than an MRI, and specialized techniques like PET scans often incur higher costs due to the use of radioactive tracers and specialized equipment. Patients should consult their healthcare providers and insurance companies for precise cost estimates relevant to their situation.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| CT Scan (Brain) | Hospitals, Imaging Centers | $270 - $5,000 |
| MRI Scan (Brain) | Hospitals, Imaging Centers | $1,000 - $8,000 |
| PET Scan (Brain) | Specialized Imaging Centers | $3,000 - $10,000 |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The evolution of imaging techniques has revolutionized the detection and management of cerebral masses, providing unprecedented clarity into the brain’s complex architecture. From initial diagnosis to guiding intricate neurosurgery and monitoring treatment responses, these technologies are fundamental to modern neurological and oncological care. Continued research and development in medical imaging promise even more precise and accessible tools for the future, further enhancing the prognosis and quality of life for patients facing these challenging conditions.




