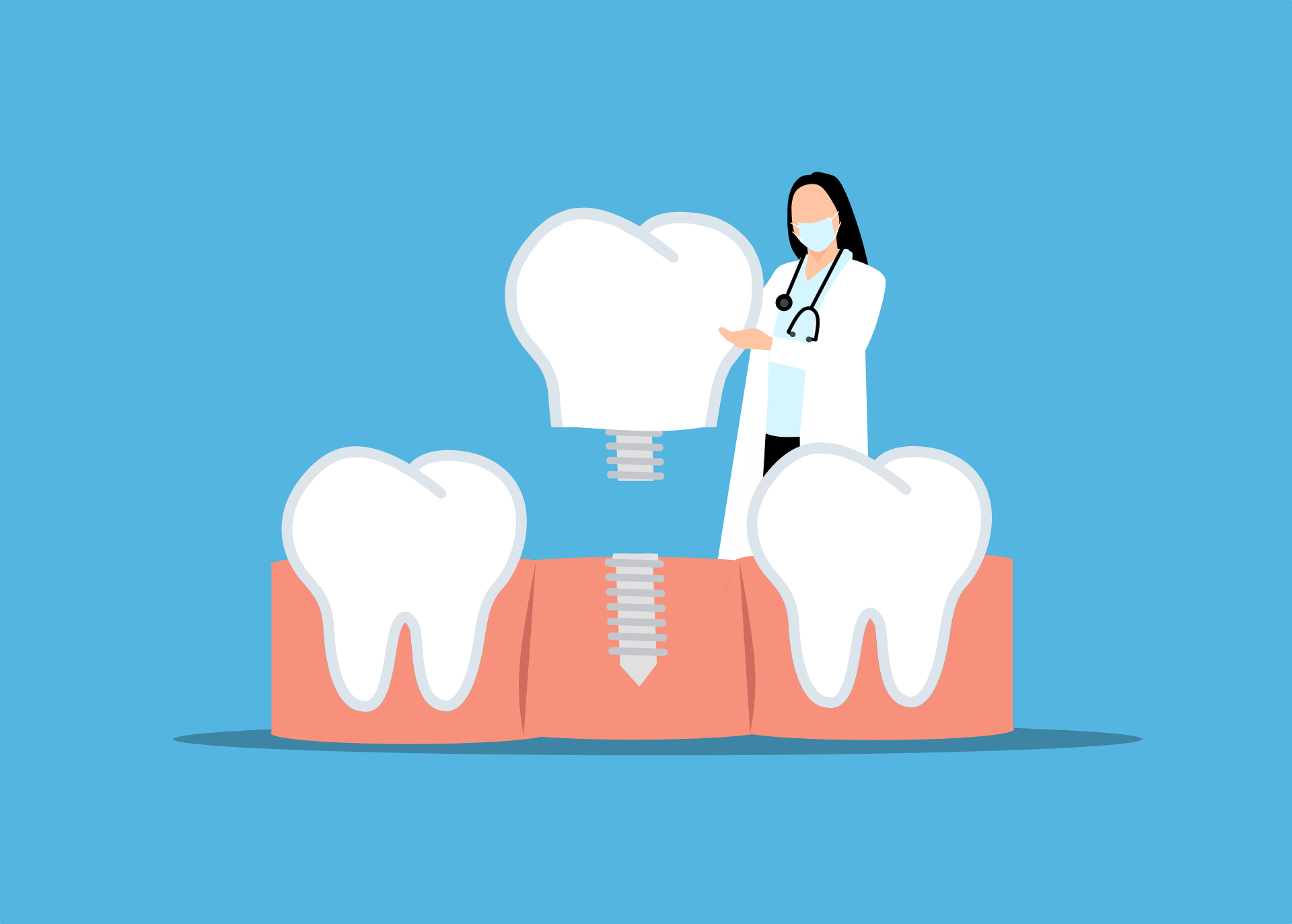
Dental Bridges: Options, Procedure, and Cost Guide
Dental bridges are a common tooth restoration option used to replace one or more missing teeth, restore chewing function, and support a natural-looking smile. They can be fixed or removable, use adjacent teeth or implants for support, and involve materials such as ceramic crowns or zirconia crowns. Understanding how bridges compare with dental implants and crowns helps you weigh treatment, recovery, and long-term oral health implications.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
What is a dental bridge and how does it restore teeth?
A dental bridge is a prosthetic device that fills a gap where one or more teeth are missing. Traditional fixed bridges attach to natural teeth on either side of the gap using dental crowns, while implant-supported bridges anchor to dental implants placed in the jawbone. Bridges restore chewing function and help maintain alignment of adjacent teeth, preventing shifting that can affect bite and oral health.
Materials: zirconia crowns and ceramic crowns explained
Materials affect durability, appearance, and cost. Ceramic crowns and zirconia crowns are popular for bridges because they offer tooth-like color and strong wear resistance. Zirconia is known for high strength and is often used where bite force is high; ceramic options can provide superior translucency for front teeth. Discussing material choices with your dentist helps balance aesthetics, function, and long-term dental care needs.
Procedure: dental crowns, dental implants, and jawbone factors
A bridge treatment is a dental procedure that may require multiple visits. For a traditional bridge, nearby teeth are prepared and fitted with crowns to support the pontic (replacement tooth). Implant-supported bridges require surgical placement of implants into the jawbone followed by a healing period before the bridge is attached. Jawbone density, oral health, and whether you need preliminary treatments like bone grafting will influence the treatment plan and timeline.
Recovery, dental treatment aftercare, and oral health
After placement, good oral hygiene is essential. Daily brushing, flossing, and regular checks at the dental clinic help prevent decay around abutment teeth and maintain the bridge’s longevity. A dentist may recommend special floss or interdental brushes for cleaning under the pontic. Regular dental care visits also allow monitoring of the bridge, surrounding teeth, and gum health to reduce the risk of complications.
Dental cost, dental tourism, and border clinics pricing overview
Costs vary widely by region, materials, and whether the bridge is implant-supported. In many countries, traditional fixed bridges done at a private dental clinic are less costly than implant-supported options, while dental tourism and border clinics can offer lower fees for comparable procedures. Dental insurance may cover part of the treatment depending on policy terms and whether the bridge is deemed medically necessary versus cosmetic. When considering dental tourism, evaluate clinic credentials, follow-up care, and the availability of a spanish-speaking dentist or translator if language is a factor.
| Product/Service | Provider | Cost Estimation |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional fixed bridge (per unit/pontic) | Private dental clinic / general dentist | US: $1,000–$3,000; Dental tourism/border clinics: $400–$1,200 |
| Implant-supported bridge (per arch) | Specialist clinic / prosthodontist | US: $3,000–$20,000; Dental tourism: $1,200–$6,000 |
| Zirconia crown (single, used in bridges) | Dental lab / dental clinic | US: $800–$2,000; Dental tourism: $200–$600 |
| Dental tourism package (bridge + clinic services) | Dental tourism clinics / platforms | Varies widely: $1,000–$8,000 depending on scope |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
Choosing a dentist, dental clinic, and insurance considerations
Selecting the right dentist or dental clinic includes reviewing credentials, experience with tooth restoration and bridges, and whether a specialist (prosthodontist) is needed. Ask about materials (ceramic crowns vs. zirconia crowns), warranty or follow-up policies, and how the clinic handles complications. Check dental insurance coverage and whether preauthorization is required. If you are seeking treatment abroad, verify clinic accreditation, patient reviews, and options for post-treatment follow-up in your area.
Conclusion
Dental bridges remain a widely used dental treatment for replacing missing teeth and restoring a functional smile. Options range from traditional bridges using dental crowns to implant-supported solutions that interact with the jawbone. Material choices like zirconia and ceramic crowns affect appearance and durability, while costs vary by provider type and location. Discussing clinical needs, long-term oral health, and financial considerations with a qualified dentist will help determine the most appropriate path for tooth restoration.