Prefabricated Homes: How They Work and What to Expect
Prefabricated homes are reshaping residential construction with faster build times, predictable quality, and modern design flexibility. Instead of building everything on-site, components are manufactured in a controlled factory environment and then shipped for assembly. This approach reduces weather-related delays and material waste while enabling tight quality control. Whether you’re drawn to contemporary aesthetics or simply want a reliable way to manage timelines, prefabrication offers a practical route to homeownership with fewer surprises once you understand the process, options, and regulations involved.
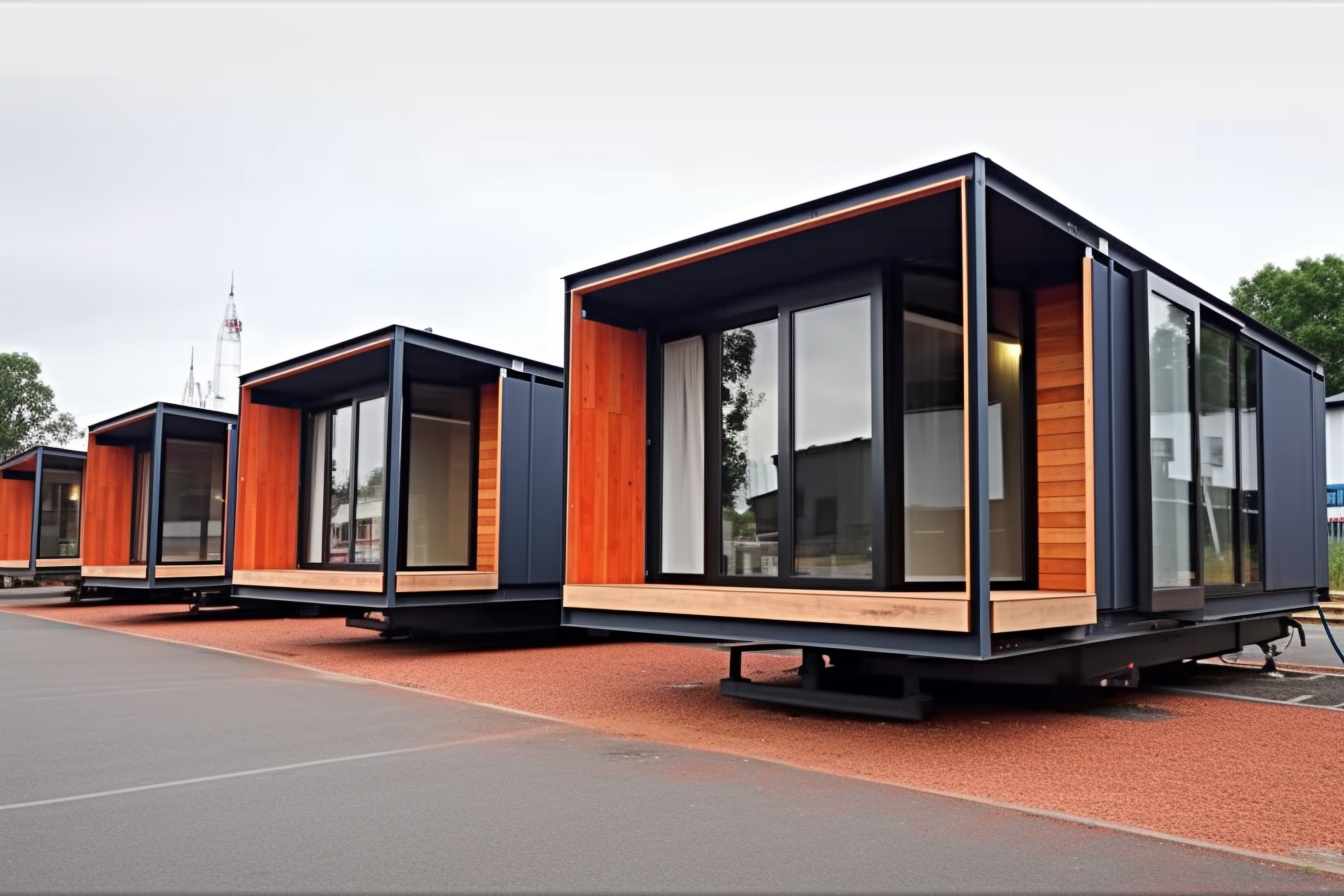

What are prefabricated homes?
A prefabricated home is built in modules or panels off-site, transported to your land, and assembled on a permanent foundation. It differs from manufactured housing, which is built on a permanent chassis under distinct federal standards. Prefab systems include modular (three-dimensional units), panelized (wall and roof panels), and kit homes (pre-cut materials packaged for assembly). Most modern prefab homes meet or exceed local building codes because they are engineered for transport, lifting, and final installation, which demands robust structural performance and repeatable quality.
Design, materials, and quality control
Design can be highly customizable, from minimalist cabins to expansive family homes. Many manufacturers offer a library of floorplans with configurable layouts, facade treatments, window placements, and energy packages. Materials often include engineered lumber, high-performance insulation, and factory-installed mechanical systems. Factory conditions lead to tighter tolerances and better fit-and-finish, which can improve airtightness and thermal performance. Selecting finishes—siding, roofing, flooring, cabinetry—usually happens before production, so your choices are integrated smoothly into the build sequence without on-site improvisation.
Construction timeline and site logistics
The timeline typically runs in parallel tracks. While the factory fabricates modules or panels in weeks, your site work proceeds: surveys, foundation, utilities, and access routes for delivery. Once the sections arrive, craning and assembly can take days, followed by mechanical hookups, exterior sealing, and interior punch-list work. Good logistics are crucial—road access, turning radius for trucks, overhead wires, and staging space all affect delivery. Planning for weather windows, crane scheduling, and local inspections helps ensure that the efficiency gains of prefabrication translate into a smooth on-site finish.
Codes, permits, and financing basics
Prefab homes must comply with the same local codes and zoning rules as site-built homes. Before ordering, verify land-use restrictions, setback requirements, height limits, and utility connections in your area. Permitting typically covers the foundation, utility tie-ins, and final occupancy. Financing can resemble conventional construction loans, with draw schedules tied to milestones like factory completion, delivery, and final inspection. Lenders may request manufacturer specifications, engineering approvals, and warranties. Coordinating early with local services—surveyors, concrete contractors, and inspectors—reduces bottlenecks and prevents costly revisions.
Using bulk_create_keyword in research? Read this first
The term bulk_create_keyword is not a meaningful search term for real-world home planning; it appears more like a placeholder used in internal content workflows. When organizing your research, use clear, descriptive tags that actually help you retrieve information later—examples include “modular-foundations,” “panelized-insulation,” or “financing-docs.” If you encounter bulk_create_keyword in a builder’s materials or online guides, treat it as a generic placeholder and replace it with topic labels specific to your project. Meaningful tagging makes it easier to compare manufacturers, track code requirements, and keep quotes and timelines organized.
Sustainability and future-proofing
Prefabrication can support sustainability goals by reducing waste and enabling precise material use. Many factories optimize cuts to minimize scrap and recycle off-cuts. Better airtightness paired with high-performance windows and insulation can lower operational energy use. If sustainability is a priority, ask about third-party certifications, VOC-low materials, heat pump systems, and solar-ready wiring. Also consider adaptability and maintenance: choose layouts that can evolve with your household, specify durable exterior cladding, and ensure easy access to mechanical systems. Thoughtful early decisions can extend the lifespan and comfort of your home.
Cost drivers and how to build a realistic budget
While exact pricing varies by region and specification, understanding the drivers helps you plan responsibly. The main components include land acquisition and preparation, foundation work, the prefab package (modules or panels), transportation and crane operations, on-site assembly and finishing, utility connections, permits and fees, and contingencies. Design complexity, finishes, energy packages, and site access can significantly affect totals. Build a contingency into your budget to account for surprises like soil remediation or utility upgrades. Seeking multiple quotes for both the home and local services can sharpen estimates and timelines.
Choosing the right manufacturer and team
Selecting a reputable manufacturer is as important as picking a floorplan. Review sample contracts, structural specs, insulation values, and warranty terms for both the factory-built components and on-site assembly. Ask for references and, if possible, tour a finished home or the factory. Evaluate communication practices—clear drawings, transparent change-order processes, and a defined schedule signal a mature operation. Equally essential is your local team: a general contractor or installer experienced with your chosen system can streamline inspections, foundation tolerances, and weatherproofing details that make the difference in the final result.
Common misconceptions to avoid
A frequent myth is that prefab homes all look identical. Factory-built does not mean cookie-cutter; customization options can be extensive, and modern manufacturers offer varied architectural styles. Another misconception is that prefab equals temporary. When placed on a proper foundation and built to local codes, a prefab home is a permanent residence. Finally, speed does not require sacrificing quality. The time savings come from parallel processes, repeatable manufacturing, and reduced weather delays, not from cutting corners on structure or safety.
Final thoughts
Prefabricated homes combine factory precision with on-site craftsmanship to deliver reliable quality and faster timelines. With careful planning—confirming codes, organizing financing, coordinating site logistics, and choosing a capable manufacturer and local team—you can reduce uncertainty and get a home that meets your design, performance, and long-term maintenance goals. Thoughtful decisions early in the process help ensure the finished home is resilient, comfortable, and aligned with your budget and lifestyle.