Fluid Power Applications in Industrial Settings
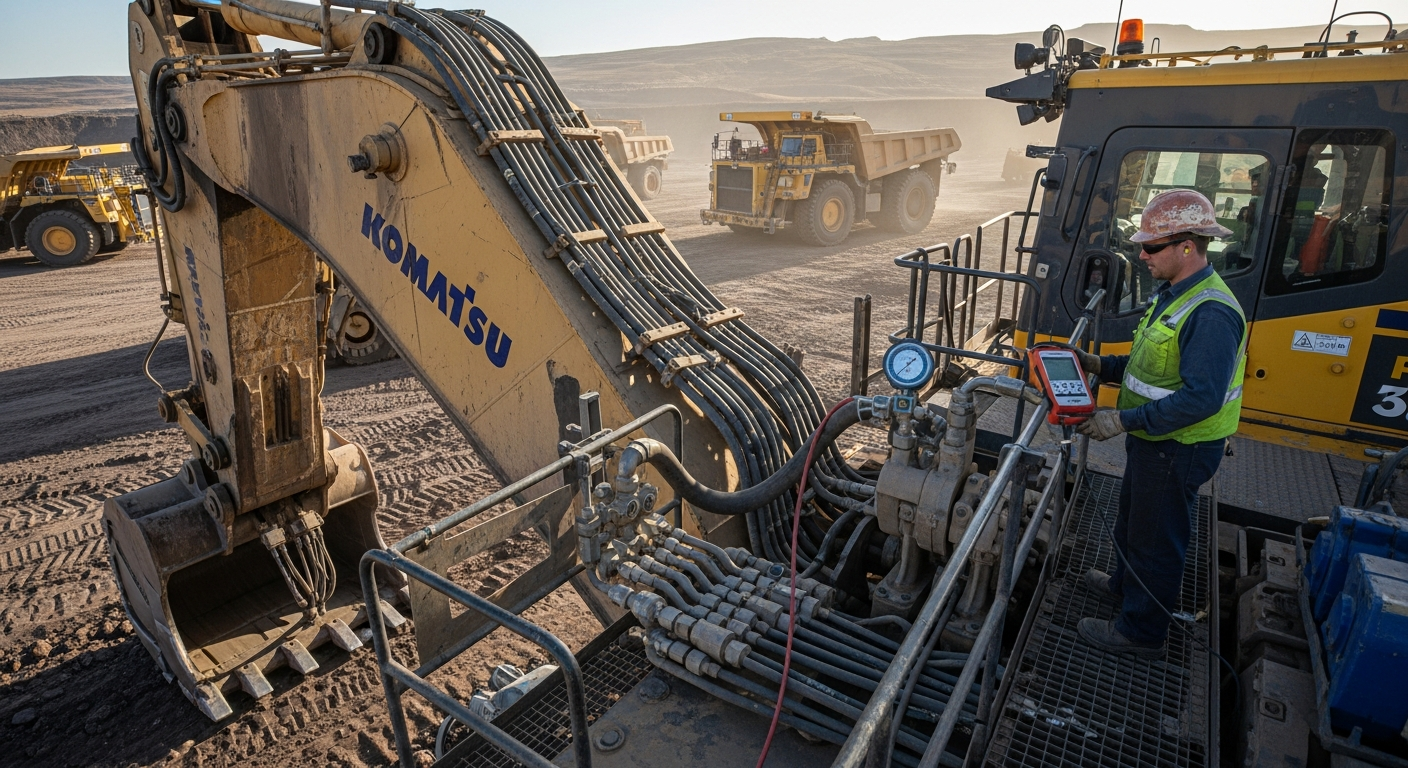
Fluid power systems are fundamental to the operation of countless industrial processes worldwide, providing the muscle behind heavy machinery and precision tools. These systems harness the power of pressurized fluids, either hydraulic oil or pneumatic air, to generate significant force and controlled motion. Their reliability and adaptability make them indispensable across various sectors, from manufacturing and construction to agriculture and material handling, ensuring efficient and robust performance in demanding environments.

Understanding Fluid Power Systems
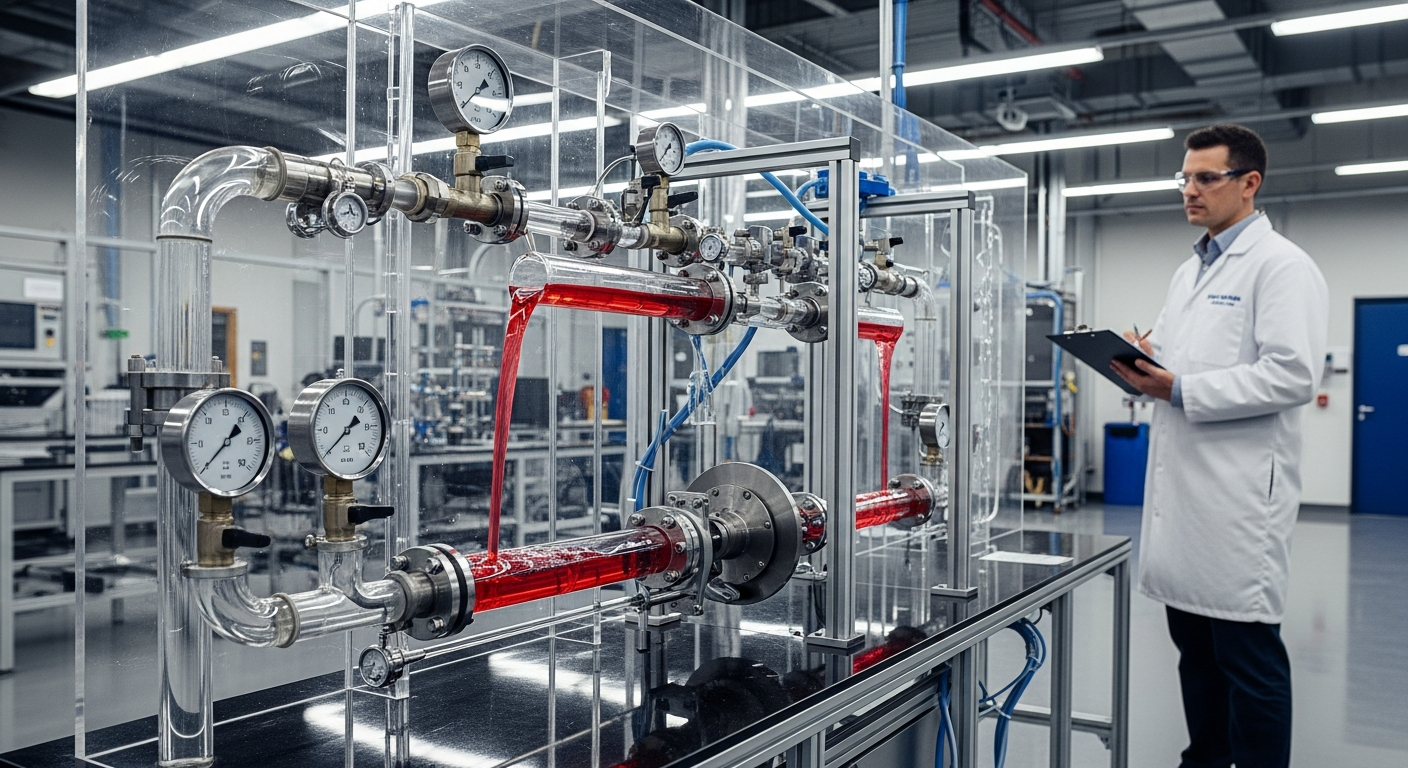
Fluid power represents a critical branch of engineering that utilizes pressurized fluids to transmit energy and control mechanical systems. This discipline is broadly categorized into hydraulics, which employs incompressible liquids like oil, and pneumatics, which uses compressible gases such as air. Both types of fluid power systems are designed to perform work by converting fluid pressure into mechanical force and motion. The fundamental principle involves a pump or compressor creating pressure within a confined fluid, which is then directed to an actuator, such as a cylinder or motor, to produce the desired linear motion or rotational movement. These systems are highly valued for their ability to generate immense power from relatively small components, offering advantages in terms of control, precision, and safety in industrial machinery.
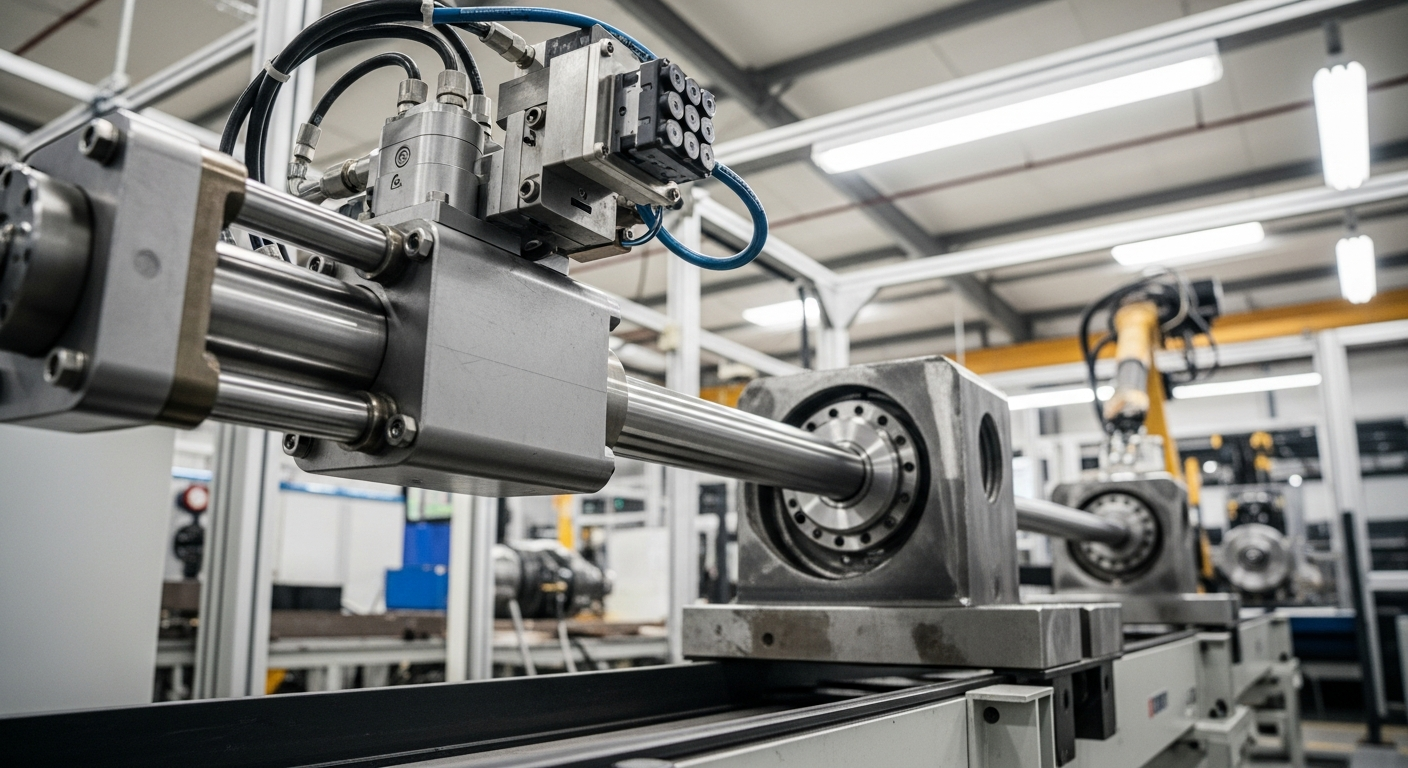
Principles of Linear Motion and Actuation in Industrial Settings
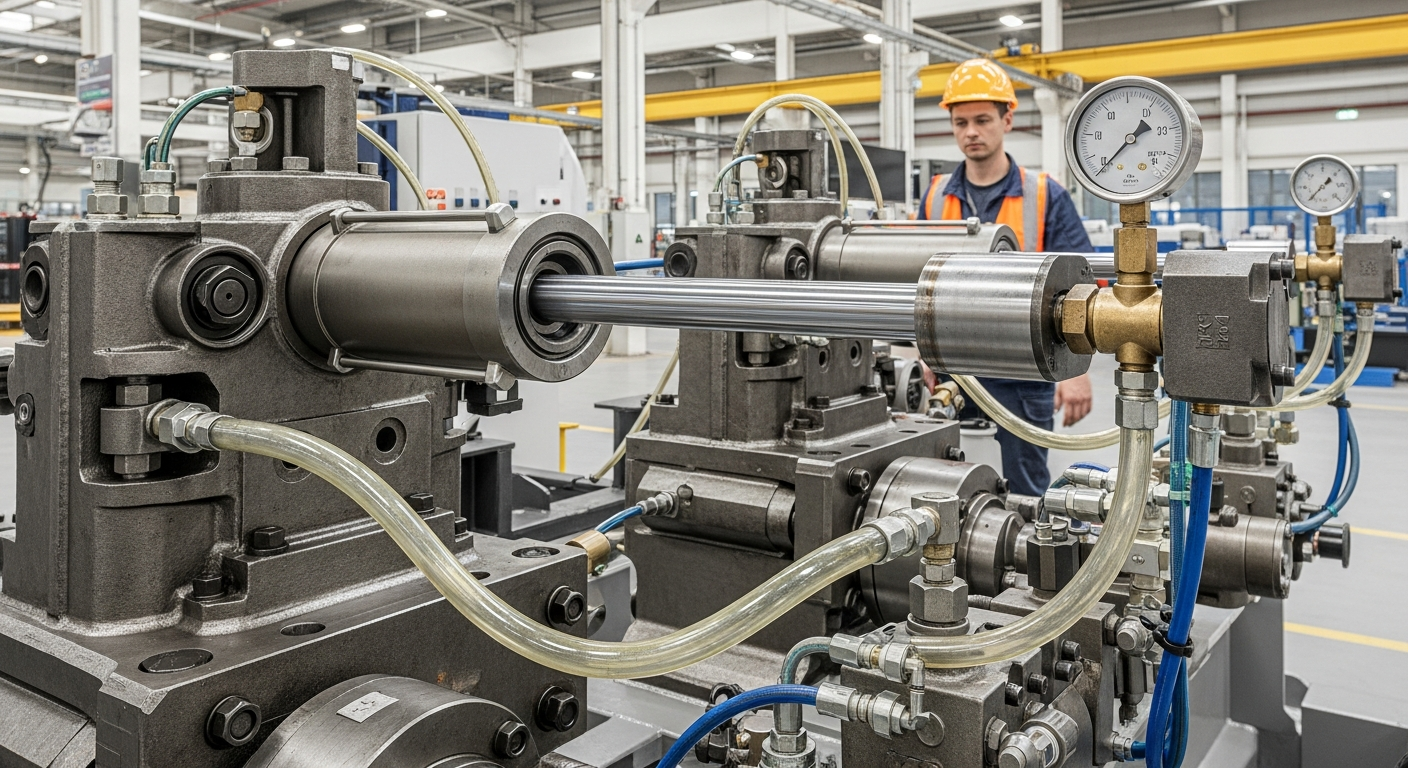
At the core of many industrial applications is the need for precise linear motion and actuation. Fluid power systems excel in this regard, particularly through the use of hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders. These components are essentially simple machines designed to convert fluid pressure into a straight-line mechanical force. When pressurized fluid enters one end of the cylinder, it pushes a piston, causing the rod to extend or retract. This controlled movement is vital for tasks like lifting heavy loads, clamping materials, pressing, and pushing in various manufacturing and processing operations. The design and engineering of these actuation devices allow for variable speeds and forces, making them adaptable to diverse operational requirements and enabling sophisticated control over industrial processes.
Industrial Applications of Fluid Power Components
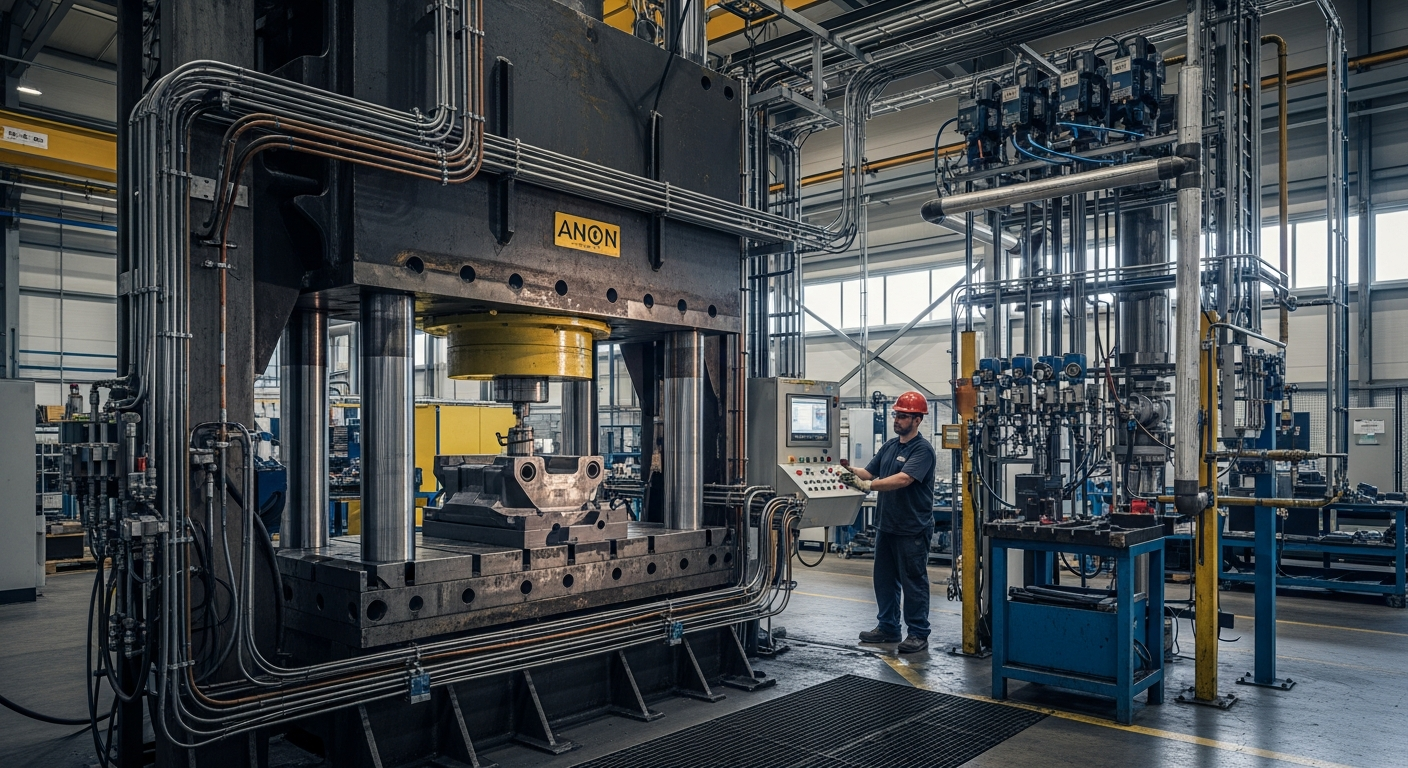
The versatility of fluid power components makes them indispensable across a wide spectrum of industrial applications. In manufacturing, hydraulic systems are commonly found in presses, injection molding machines, and robotic arms, providing the necessary force for forming and assembling machinery. Construction equipment, such as excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, relies heavily on hydraulic systems for their lifting, digging, and moving capabilities. Agricultural machinery, including tractors and harvesters, also integrates fluid power for operating implements and steering. Beyond these, fluid power plays a role in material handling, mining, aerospace, and marine engineering, demonstrating its pervasive influence. The ability to generate high forces and achieve precise control makes these systems a preferred choice for demanding tasks where reliability is paramount.
The Role of Force and Pressure in System Dynamics
The relationship between force and pressure is central to understanding the dynamics of fluid power systems. Pressure, defined as force per unit area, is the driving factor that enables these systems to perform work. By controlling the pressure of the fluid, engineers can precisely regulate the output force and speed of an actuator. For instance, in a hydraulic cylinder, the force exerted by the piston is a direct product of the fluid pressure and the piston’s surface area. This principle allows for the design of systems that can generate enormous forces required for heavy-duty industrial tasks, while also maintaining fine control for delicate operations. Careful engineering of valves, pumps, and reservoirs ensures that pressure is maintained and directed efficiently throughout the entire system, optimizing performance and energy usage.
Advancements in Fluid Power for Automation
Modern industrial environments increasingly demand higher levels of automation and efficiency. Fluid power systems have evolved significantly to meet these needs, integrating advanced control technologies and smart components. The incorporation of sensors, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and sophisticated electronic controls allows for real-time monitoring and precise management of fluid pressure, flow, and actuator position. This integration enhances the accuracy, repeatability, and diagnostic capabilities of machinery, facilitating seamless operation within automated production lines. Innovations in fluid dynamics and material science also contribute to more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly systems, reducing energy consumption and extending the lifespan of equipment. These advancements underscore the continued relevance of fluid power in the era of Industry 4.0, driving further innovation in industrial engineering.
| Provider Name | Services Offered | Key Features/Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bosch Rexroth | Hydraulic cylinders, pumps, valves, power units | High-performance, energy-efficient, customizable |
| Parker Hannifin | Hydraulic cylinders, hoses, fittings, filtration | Broad product range, global support, robust design |
| Eaton | Industrial hydraulics, mobile hydraulics | Reliable, durable, integrated solutions |
| Danfoss | Mobile hydraulics, industrial components | Advanced control, compact design, high power density |
| Enerpac | High-pressure hydraulic tools, cylinders, pumps | Heavy lifting, pushing, pulling applications |
Fluid power systems remain a cornerstone of industrial engineering, providing robust and reliable solutions for generating force and motion. Their ability to achieve precise linear motion and actuation through controlled pressure makes them indispensable across diverse sectors. As automation continues to advance, the integration of smart technologies with traditional fluid power systems ensures their continued evolution and importance in driving the efficiency and capabilities of industrial machinery and equipment worldwide. The ongoing developments in system dynamics and components promise even greater adaptability and performance in future industrial applications.