Designing Robust Systems for Linear Force Transmission
Hydraulic cylinders are fundamental components in countless industrial and mobile applications, serving as the muscle behind many operations that require significant linear force. These devices efficiently convert hydraulic fluid power into mechanical linear motion, enabling heavy lifting, precise positioning, and powerful pressing actions across various sectors. Understanding their operational principles and design considerations is crucial for engineers and technicians aiming to develop reliable and high-performance systems.

Understanding the Fundamentals of Fluid Power Actuation
Hydraulic cylinders operate on the principle of fluid power, where incompressible fluid, typically oil, is pressurized and directed to move a piston within a cylindrical bore. This mechanism generates substantial linear force, making them indispensable in applications requiring powerful and controlled movement. The fluid’s pressure acting on the surface area of the piston creates the force, which is then transmitted through a piston rod to perform work. This efficient conversion of hydraulic energy into mechanical energy is central to their widespread use in various industrial machinery and mobile equipment.
How Hydraulic Cylinders Generate Linear Motion and Force
The core function of a hydraulic cylinder is to provide controlled linear motion and force. When hydraulic fluid is pumped into one side of the cylinder, it pushes the piston, causing the piston rod to extend or retract. The direction of motion is determined by which port the fluid enters. In a double-acting cylinder, fluid can be directed to either side of the piston, allowing for both extension and retraction under hydraulic power. This precise control over the piston’s movement is critical for tasks that demand accuracy and repeatability, such as those found in manufacturing and engineering processes. The amount of force produced is directly proportional to the fluid pressure and the effective surface area of the piston.
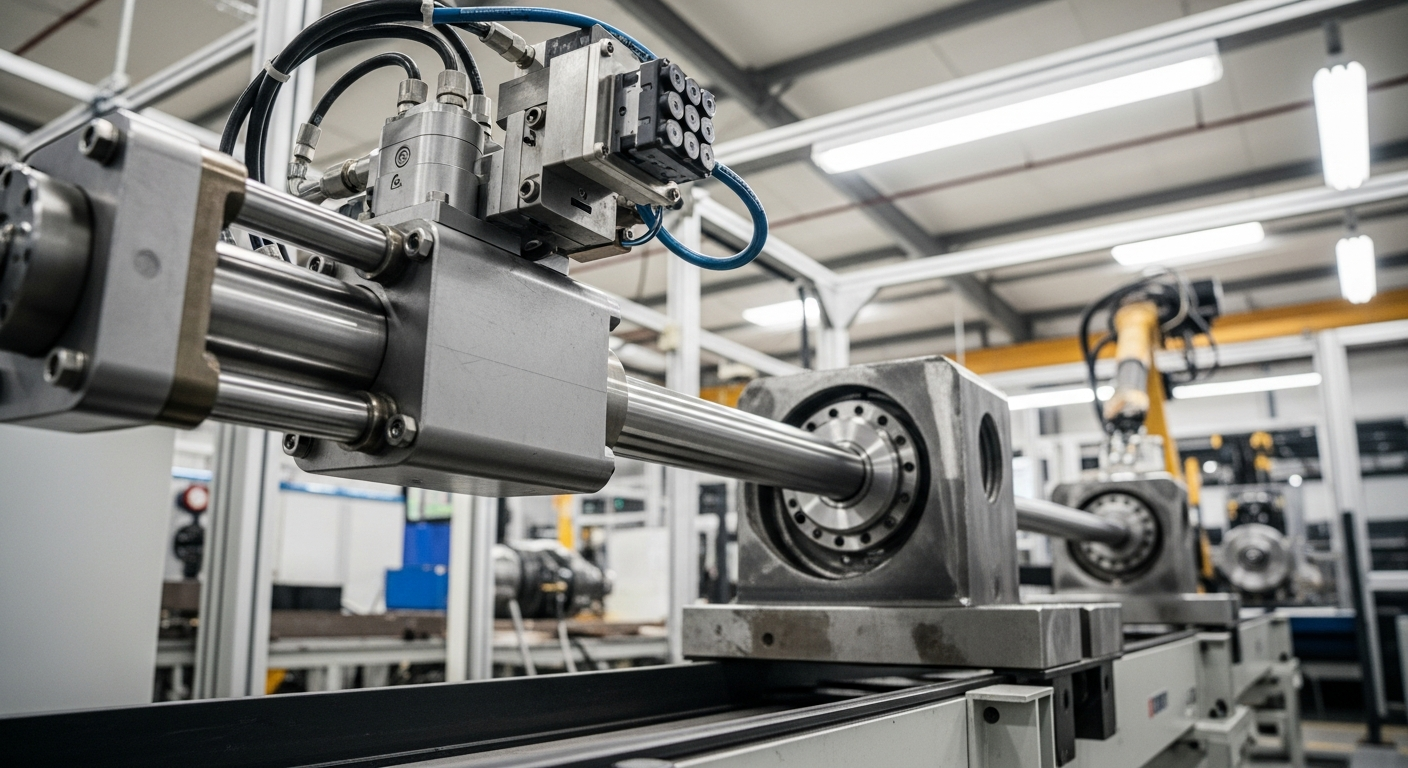
Key Components and Operational Principles of Drive Systems
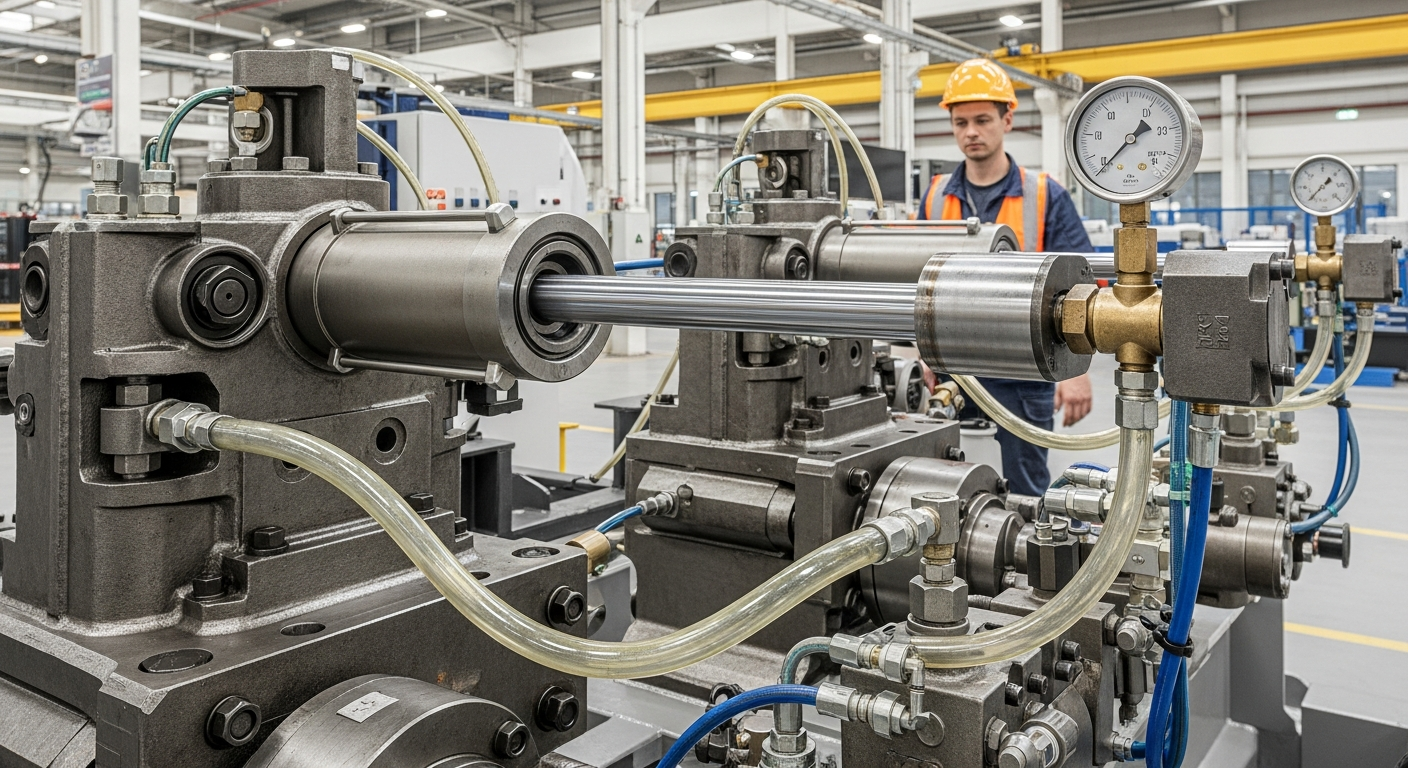
A typical hydraulic cylinder system comprises several key components working in concert. The cylinder barrel, often made from honed steel, houses the piston, which is sealed to prevent internal leakage. The piston rod connects the piston to the external load, transmitting the generated force. Seals, both static and dynamic, are crucial for maintaining pressure and preventing fluid loss. Hydraulic fluid enters and exits the cylinder through ports, controlled by a hydraulic drive system that includes a pump, valves, and a reservoir. The pump generates the necessary pressure, while the valves direct the fluid flow, enabling precise control over the cylinder’s actuation and the overall system’s performance.
Applications in Industrial Machinery and Manufacturing
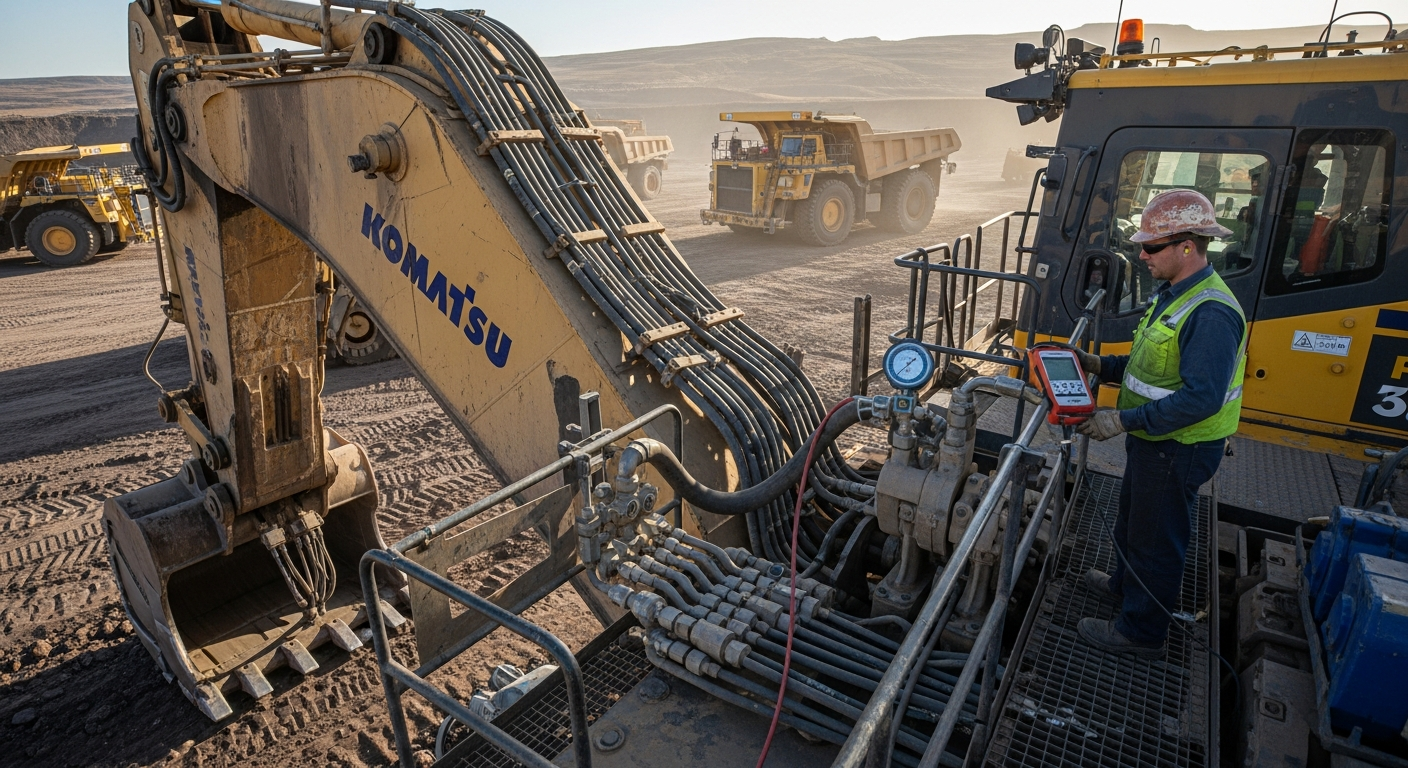
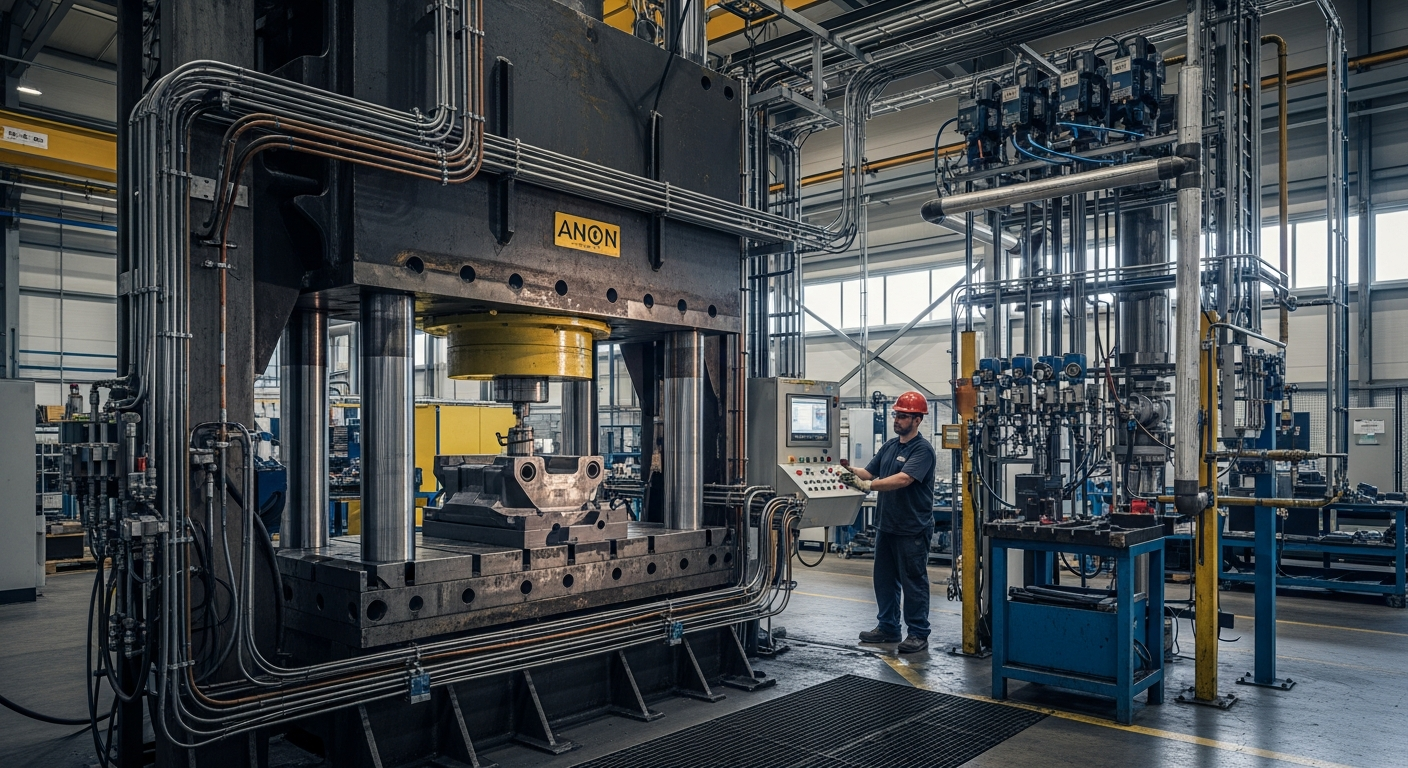
Hydraulic cylinders are vital for industrial machinery and manufacturing operations due to their ability to deliver high force and precise control. They are commonly found in presses, injection molding machines, and material handling equipment, where they facilitate tasks like clamping, lifting, and compacting. In construction, they power excavators, loaders, and cranes. Their robust design allows them to withstand harsh operating conditions and heavy loads, making them a preferred choice for heavy-duty applications. The reliability and efficiency of hydraulic actuation contribute significantly to productivity and operational safety in these demanding environments.
Considerations for Robust Hydraulic Cylinder Engineering and Control
Designing robust hydraulic cylinder systems involves careful consideration of several engineering factors. Engineers must select cylinders with appropriate bore and rod diameters to achieve the required force and speed while ensuring structural integrity under maximum operating pressure. Material selection for the cylinder barrel, piston, and rod is critical for durability and resistance to wear and corrosion. The choice of seals impacts efficiency and longevity. Furthermore, integrating advanced control systems, including proportional valves and sensors, allows for fine-tuning of motion, velocity, and force, enhancing the overall precision and responsiveness of the hydraulic system. Proper maintenance and regular inspection are also essential to ensure long-term reliability and performance in any industrial setting.
Hydraulic cylinders are indispensable components for converting fluid power into linear motion and substantial force. Their robust design, coupled with precise control mechanisms, makes them suitable for a vast array of demanding applications across various industries. From heavy industrial machinery to intricate manufacturing processes, these devices play a critical role in enabling powerful and controlled actuation, underscoring their importance in modern engineering and drive systems.