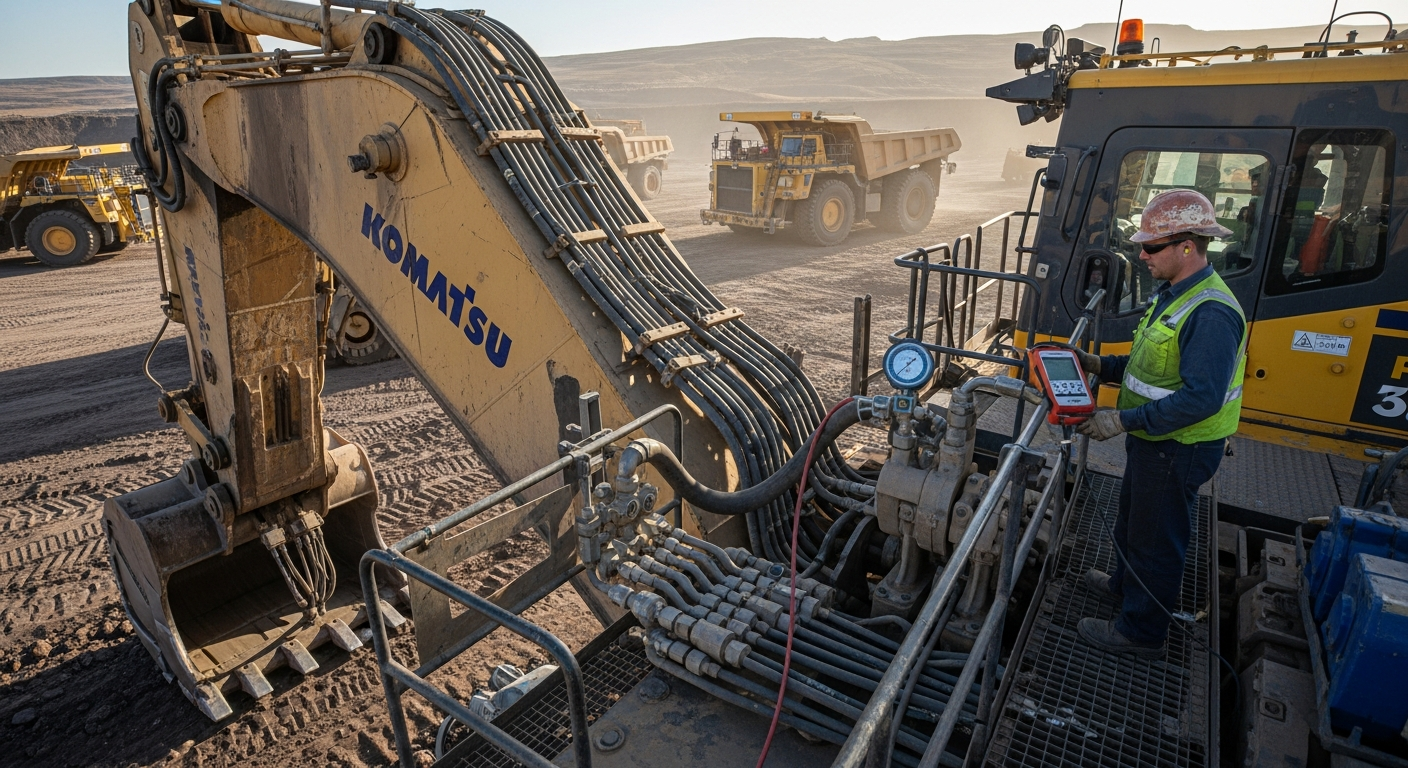
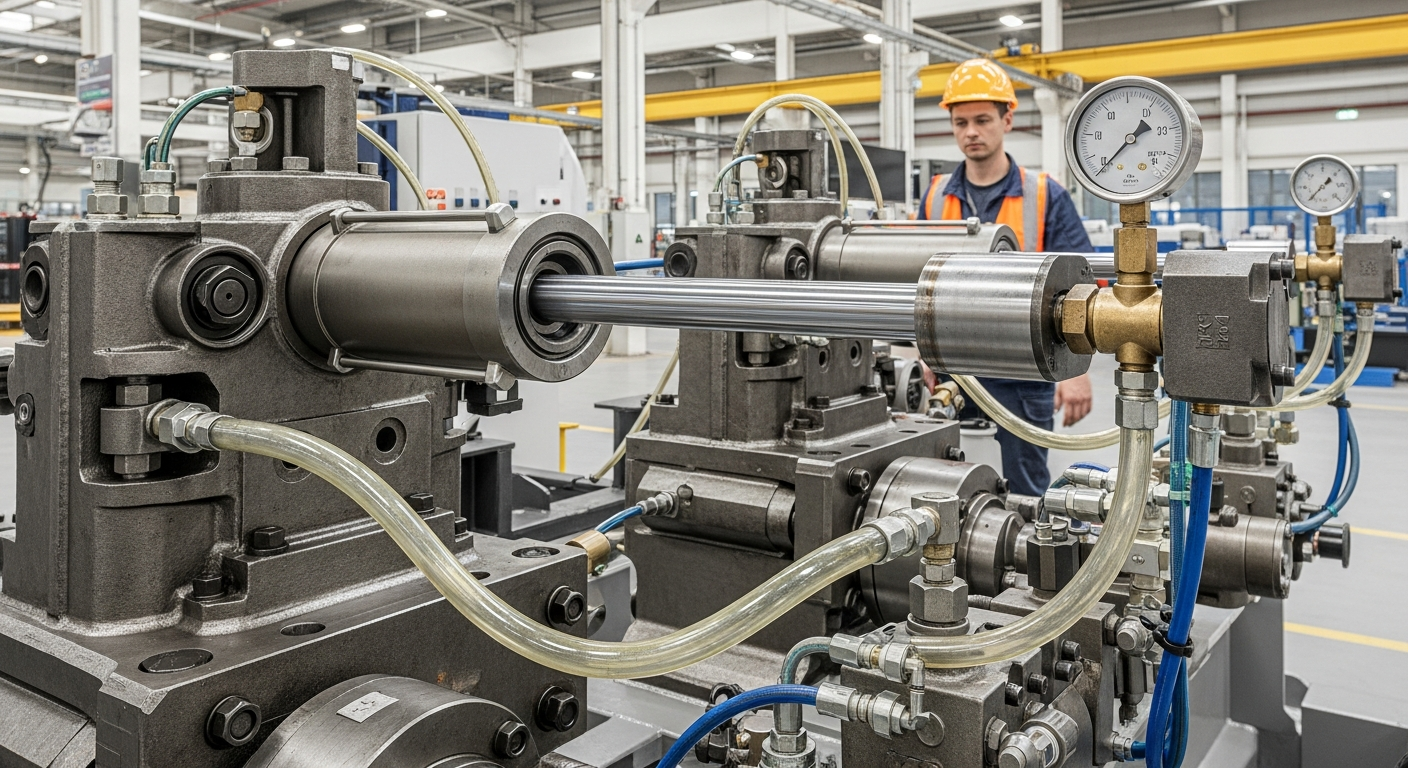
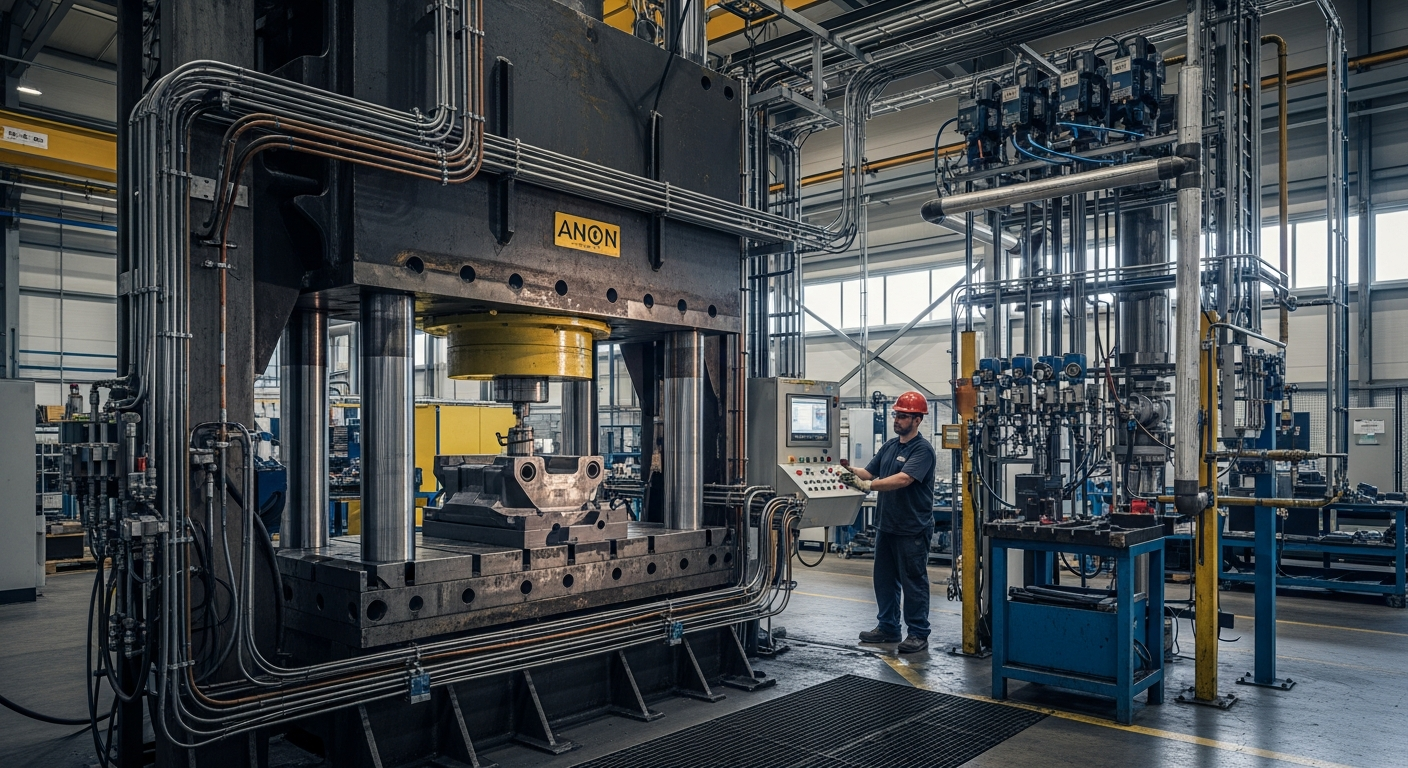
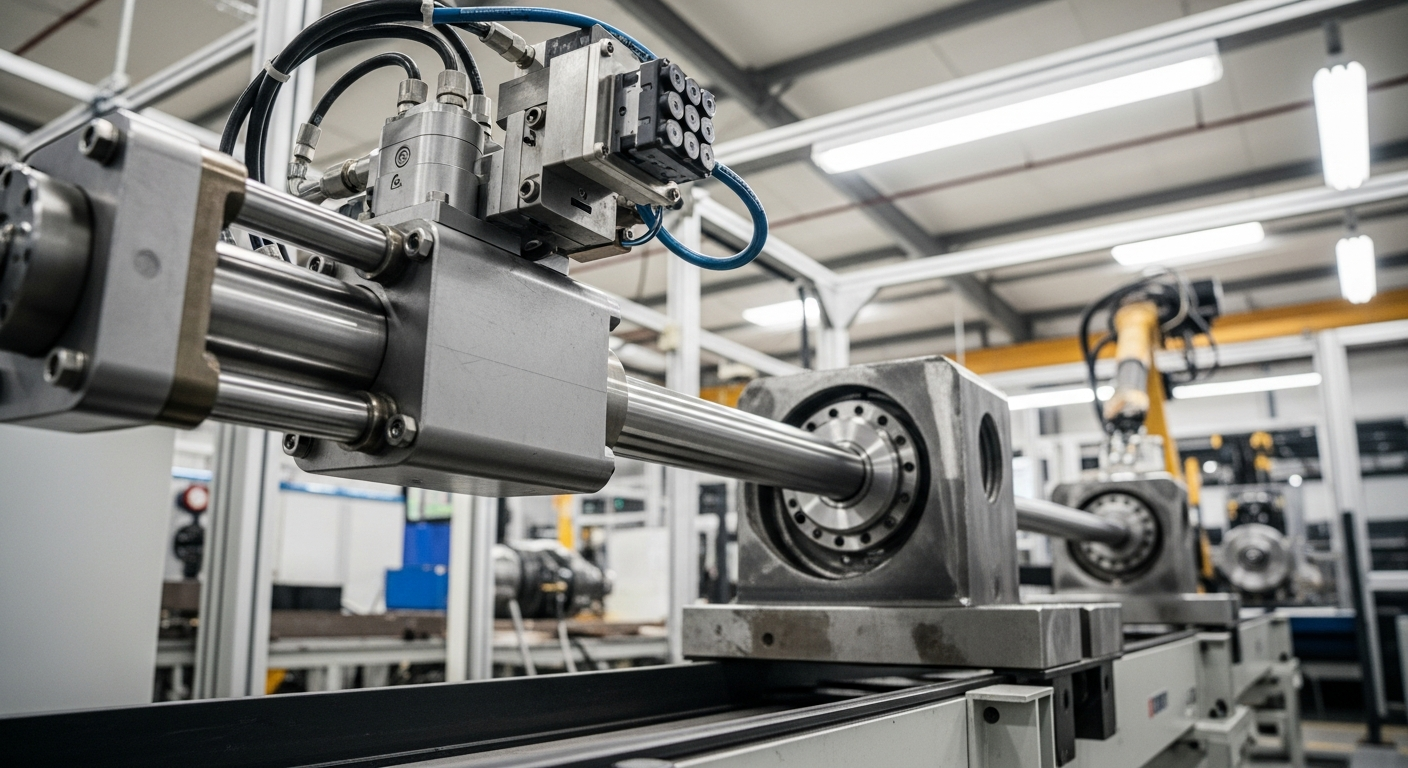
The Role of Fluid Mechanics in Machine Performance
Fluid mechanics, a fundamental branch of physics, plays a critical role in the design, operation, and efficiency of modern industrial machinery. Its principles govern how liquids and gases behave under various conditions, directly influencing the performance of systems that rely on fluid power. Understanding these mechanics is essential for engineers to develop robust, precise, and powerful equipment capable of executing demanding tasks across numerous sectors, from manufacturing to construction. This foundational knowledge ensures that components like cylinders and pumps operate effectively, translating fluid energy into controlled mechanical work.
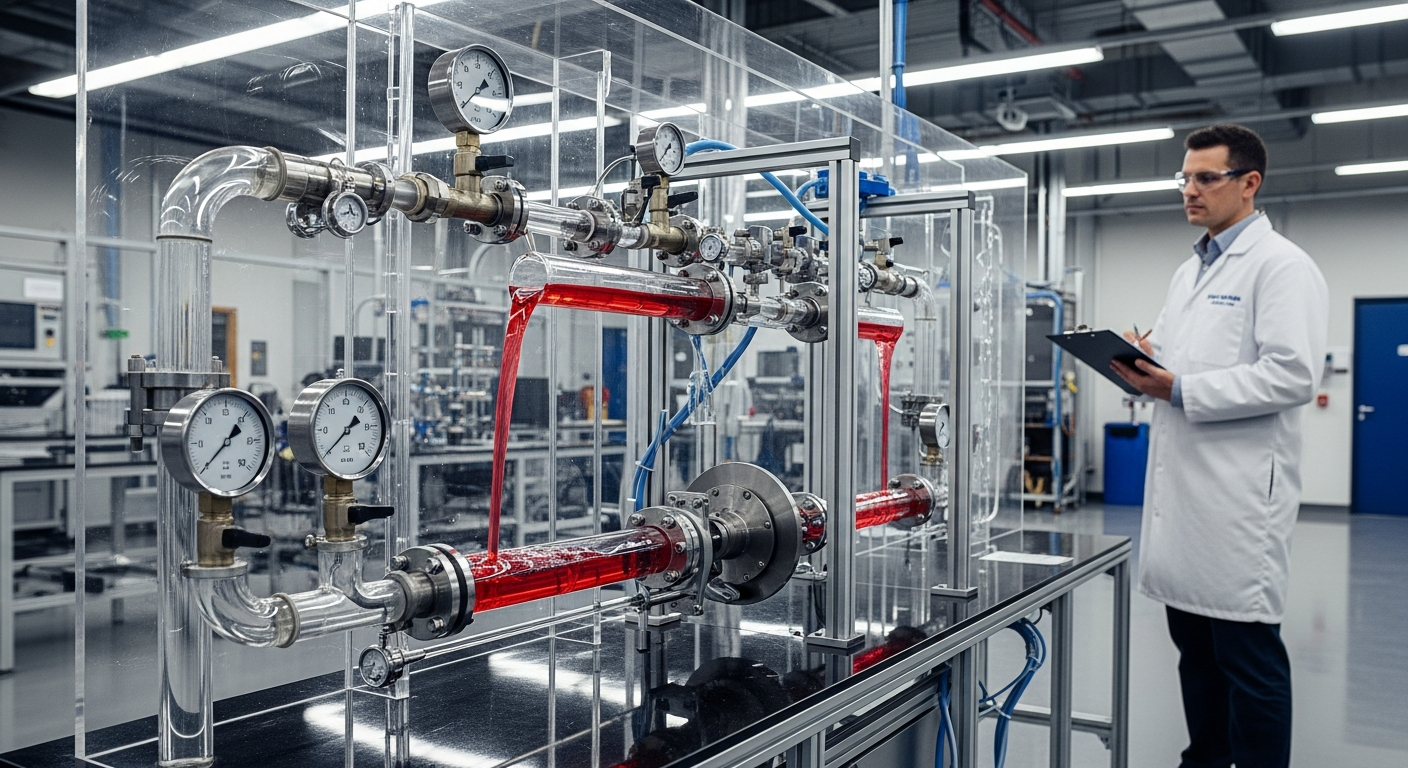

Fluid mechanics is the study of fluids and the forces on them. In the context of industrial machinery, this scientific discipline is indispensable for understanding how power is generated, transmitted, and controlled. Systems that harness fluid power, often using incompressible liquids, are central to many applications requiring significant force and precise control. The ability to generate substantial force from relatively small inputs is a hallmark of these engineering systems, contributing to the widespread use of such equipment in manufacturing and automation.
Principles of Fluid Power for Industrial Actuation
At the core of many industrial applications is the principle of linear actuation, where fluid pressure is converted into a straight-line mechanical force and movement. This involves components designed to contain and direct fluid under pressure, enabling the precise control of machinery. The application of fluid mechanics allows for the generation of immense force, making it possible to lift heavy loads, press materials, and perform other strenuous tasks that would be impractical or impossible with purely mechanical linkages. Understanding how fluid pressure translates into motion is key to designing effective industrial equipment.
Harnessing Pressure for Controlled Movement
Pressure within a fluid system is the primary driver for generating the necessary force. By applying pressure to a fluid, energy is transferred, which can then be used to create controlled motion. This control is crucial in modern industrial machinery, where accuracy and repeatability are paramount. Engineering systems are meticulously designed to manage fluid flow and pressure, ensuring that movement is smooth, predictable, and responsive to operational commands. This precise control allows for sophisticated automation processes, improving overall operational efficiency.
Optimizing Efficiency in Manufacturing Equipment
Efficiency is a critical consideration in all industrial applications, particularly in manufacturing. Fluid mechanics contributes significantly to the efficiency of equipment by enabling high power-to-weight ratios and minimizing energy loss. The design of fluid pathways, seals, and actuating components directly impacts how effectively fluid energy is converted into useful work. Continuous advancements in the field aim to reduce friction, prevent leaks, and optimize fluid flow, thereby enhancing the overall performance and sustainability of industrial machinery and automation systems. These improvements lead to reduced operational costs and increased productivity.
The Role of Systems and Components in Performance
Every component within a fluid power system plays a vital role in its overall performance. From pumps that generate pressure to valves that control flow and cylinders that provide the linear motion, each element must function in harmony. The selection of materials, the precision of manufacturing, and the integration of these parts into a cohesive system are all governed by principles of engineering and fluid mechanics. This integrated approach ensures that the machinery can withstand demanding industrial environments while delivering consistent and reliable actuation and force for various tasks.
Advancements in Fluid Mechanics for Automation
Modern industrial operations increasingly rely on advanced automation, where fluid mechanics continues to evolve. Innovations in control systems, sensor technology, and material science are constantly improving the capabilities of fluid-powered equipment. These advancements allow for more sophisticated movement sequences, greater precision in force application, and enhanced diagnostic capabilities. The integration of digital control with traditional fluid power principles opens new possibilities for complex manufacturing processes and intelligent machinery, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in industrial engineering.
In summary, fluid mechanics is an indispensable discipline underpinning the functionality and performance of industrial machinery. Its principles enable the generation of significant force, precise control of motion, and enhanced operational efficiency. As industries continue to evolve, the application of fluid mechanics will remain central to developing innovative and powerful equipment, driving progress in manufacturing, automation, and various other sectors worldwide.