The engineering behind controlled linear movement
Hydraulic cylinders are fundamental components in a vast array of machinery, translating fluid power into precise linear motion. Their ability to generate substantial force and provide reliable, controlled movement makes them indispensable across numerous industries. Understanding the engineering principles and operational mechanics behind these robust devices reveals their critical role in modern industrial and mechanical applications, enabling everything from heavy lifting to intricate automation.
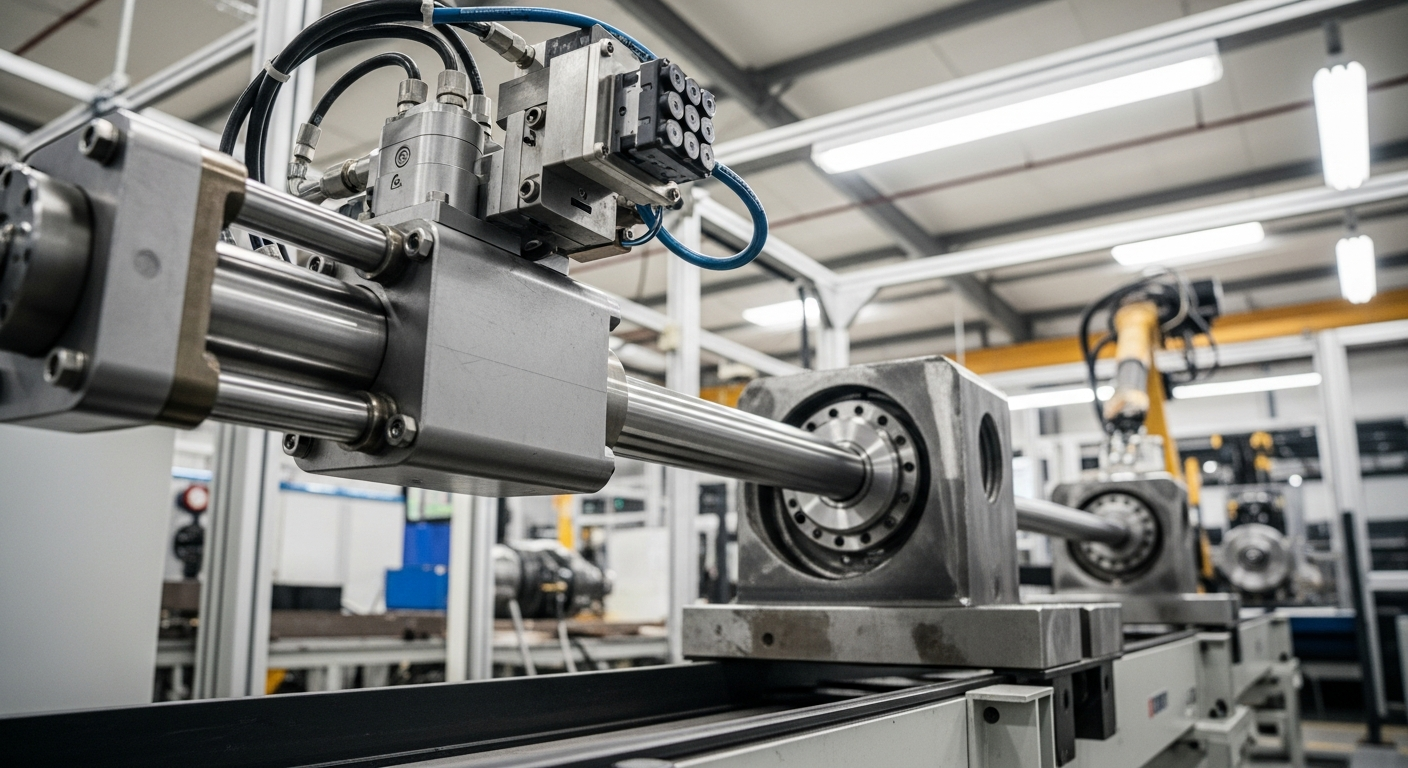
Understanding Fluid Power and Actuators
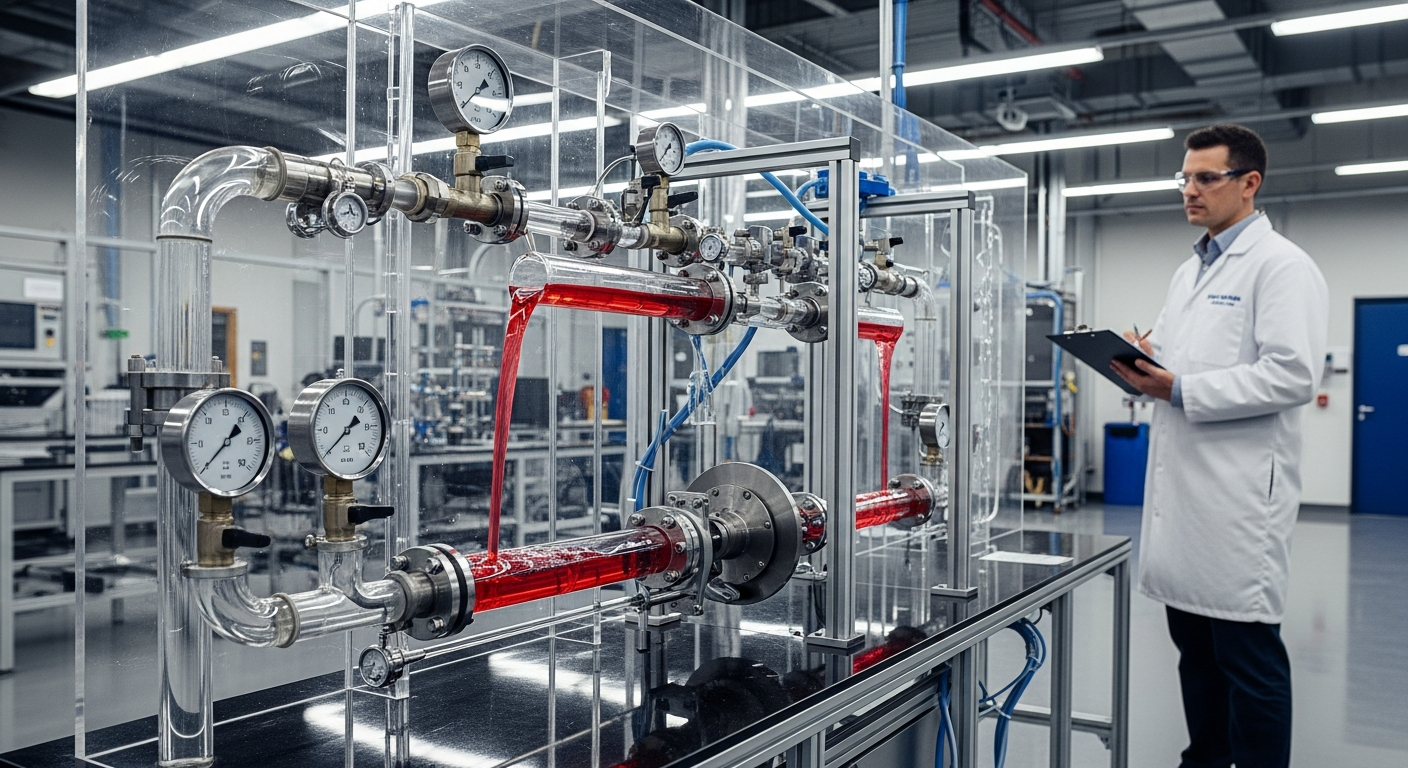
Hydraulic cylinders operate on the principle of fluid power, specifically hydraulics, which involves the use of pressurized liquid to transmit energy. As key actuators in many engineering systems, they convert hydraulic pressure into a linear mechanical force or motion. This process begins when a non-compressible fluid, typically hydraulic oil, is pumped into the cylinder, exerting pressure on a piston. The piston then moves along the cylinder barrel, extending or retracting a rod, thereby performing work. This efficient conversion of fluid energy to linear mechanical energy is what makes hydraulic cylinders so powerful and versatile, forming the backbone of many industrial operations worldwide.
Core Components and Operational Mechanics
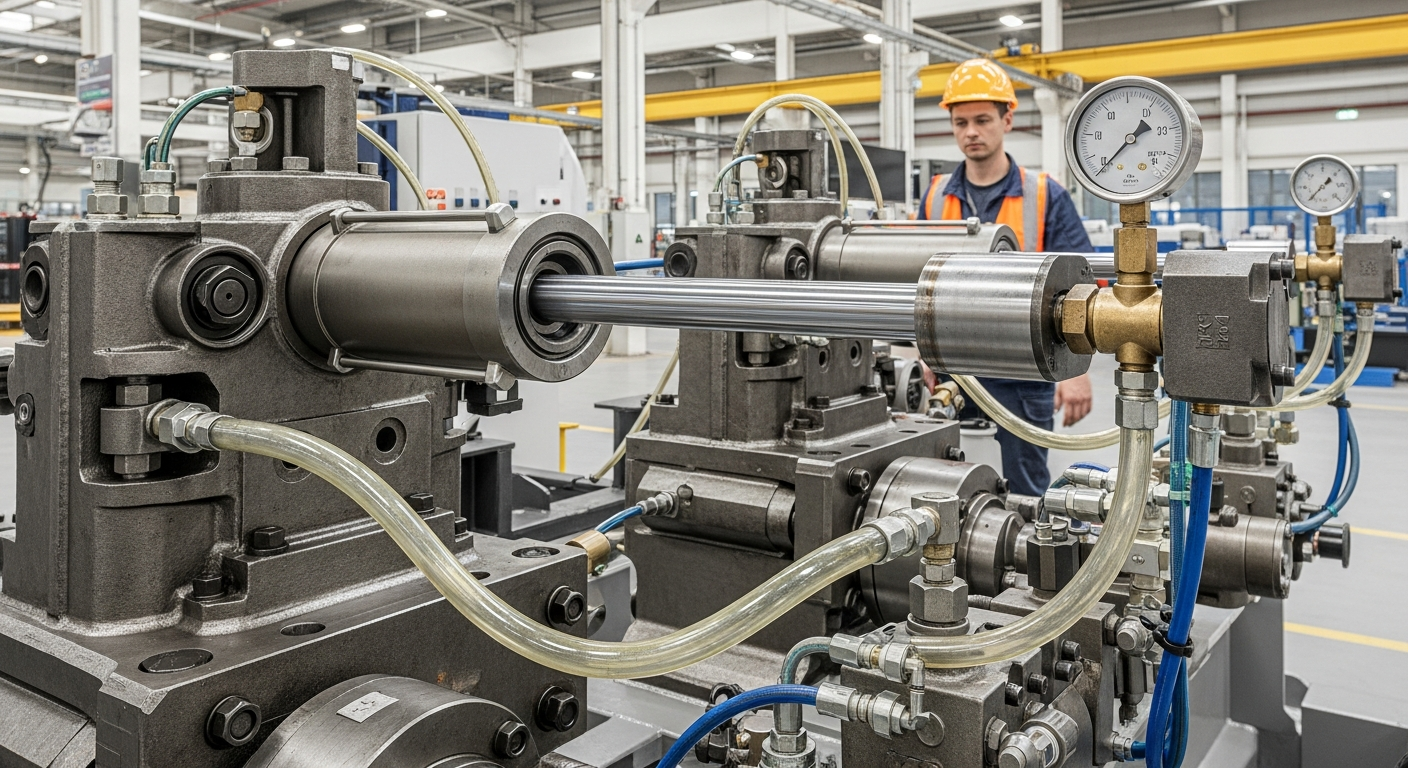
The fundamental design of a hydraulic cylinder includes several key components that work in concert to achieve controlled linear movement. The main parts consist of a cylinder barrel, a piston, a piston rod, and various seals and ports. The barrel is a precision-honed tube that houses the piston. The piston divides the barrel into two chambers, and the piston rod extends from one side of the piston, transferring the mechanical force externally. Seals are crucial for preventing fluid leakage and maintaining pressure integrity. When hydraulic fluid is introduced into one chamber, it pushes the piston, causing the rod to extend or retract. Controlling the direction and volume of fluid flow allows for precise control over the speed and direction of the cylinder’s motion, making them vital systems in mechanics.
Applications in Industrial and Manufacturing Settings
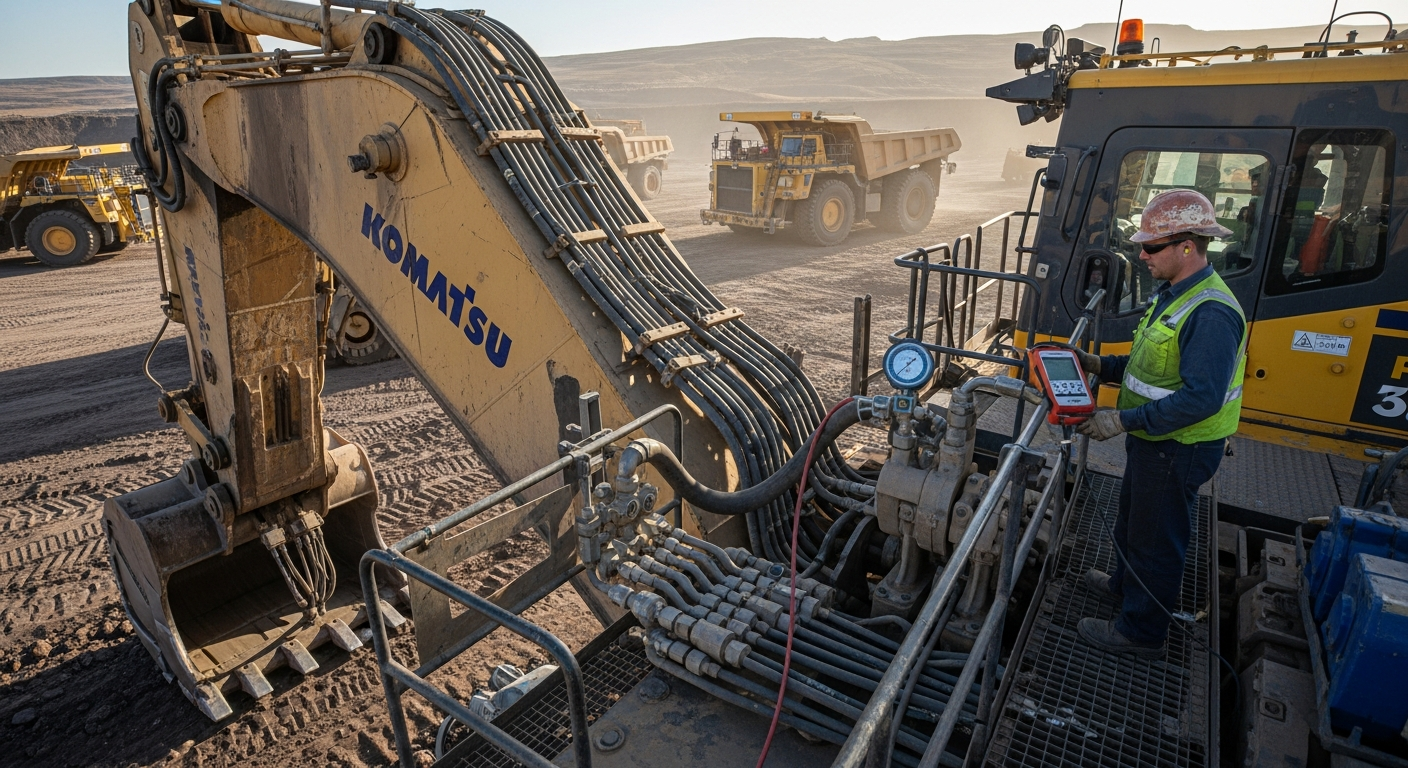
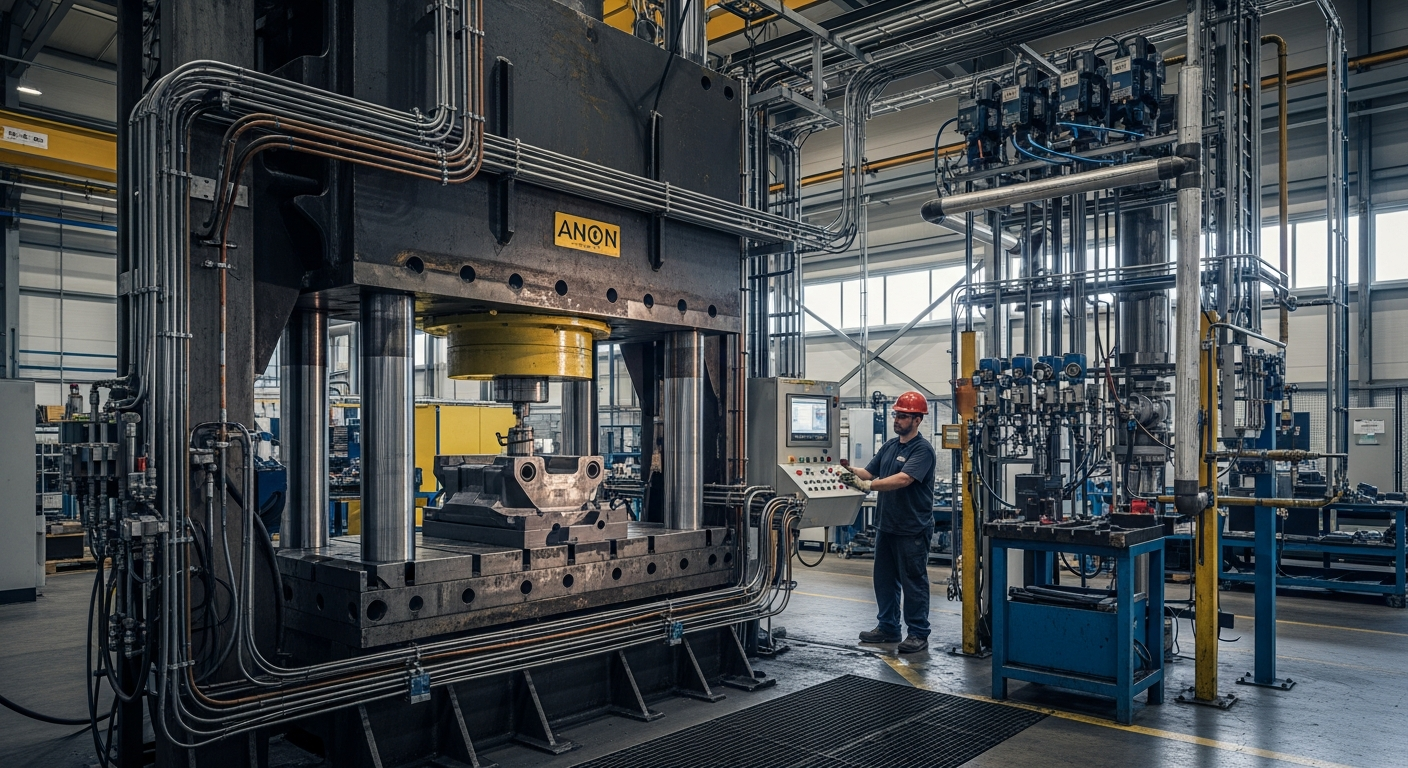
In industrial environments, hydraulic cylinders are ubiquitous, providing the necessary power for a wide range of tasks. They are integral to manufacturing processes, driving presses, clamping mechanisms, and assembly line equipment. Their capacity to generate high force in a compact design makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications, where consistent and reliable lifting or pushing capabilities are essential. From metal forming to material handling, these cylinders ensure efficient operation, contributing significantly to productivity and safety within factories and production facilities. The robust nature of these components allows them to withstand demanding conditions, making them a preferred choice for heavy machinery.
Diverse Uses in Construction and Agriculture
Hydraulic cylinders are indispensable in sectors like construction and agriculture, where large-scale lifting and pushing tasks are daily occurrences. In construction, they power the booms, buckets, and blades of excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, enabling earthmoving, demolition, and material placement. Similarly, in agriculture, these equipment are central to the operation of tractors, harvesters, and other farm machinery, facilitating tasks such as raising and lowering implements, steering, and operating attachments. Their ability to deliver consistent and powerful motion under varying loads and environmental conditions underscores their critical role in these demanding fields, enhancing efficiency and operational capabilities.
Integrating Hydraulic Cylinders in Automation and Control Systems
The precision and control offered by hydraulic cylinders make them key components in modern automation systems. Paired with advanced control valves and sensors, they can execute highly accurate and repeatable motion profiles. This level of control is vital in applications requiring exact positioning or specific force application, such as robotic arms or automated assembly lines. The ability to finely regulate the pressure and flow of hydraulic fluid allows engineers to program complex sequences of movements, significantly improving the efficiency and consistency of automated processes. This integration of fluidpower with sophisticated electronic systems allows for dynamic adjustments and real-time feedback, optimizing performance.
Maintenance and Performance Considerations for Hydraulic Equipment
Ensuring the longevity and optimal performance of hydraulic cylinders within machinery and equipment requires diligent maintenance and careful consideration of operational factors. Regular inspection of seals, hydraulic fluid levels, and overall system integrity is paramount to prevent leaks and maintain efficient pressure transmission. The quality of the hydraulic fluid directly impacts the cylinder’s performance and lifespan, as contaminants can cause wear and reduce efficiency. Proper sizing of cylinders for specific force and motion requirements is also crucial in the initial engineering design phase to prevent premature failure and ensure adequate power delivery. Adhering to manufacturer guidelines for service intervals and using appropriate replacement components can significantly extend the operational life of these vital systems.
Hydraulic cylinders are a testament to effective engineering, converting fluid pressure into versatile linear mechanical force. Their widespread application across heavy industries, construction, agriculture, and automated systems highlights their indispensable role in modern technology. The continued development of these robust components ensures that they will remain central to the advancement of controlled motion and power delivery in various fields for the foreseeable future.




