Understanding Mechanical Energy Conversion Devices
Mechanical energy conversion devices are fundamental to numerous industries, transforming one form of energy into another to perform work. Among these, hydraulic cylinders stand out as critical components, adept at converting fluid power into linear mechanical force and motion. Their robust design and operational efficiency make them indispensable in a vast array of applications, from heavy construction equipment to intricate manufacturing processes, enabling precise control and powerful actuation in demanding environments worldwide.
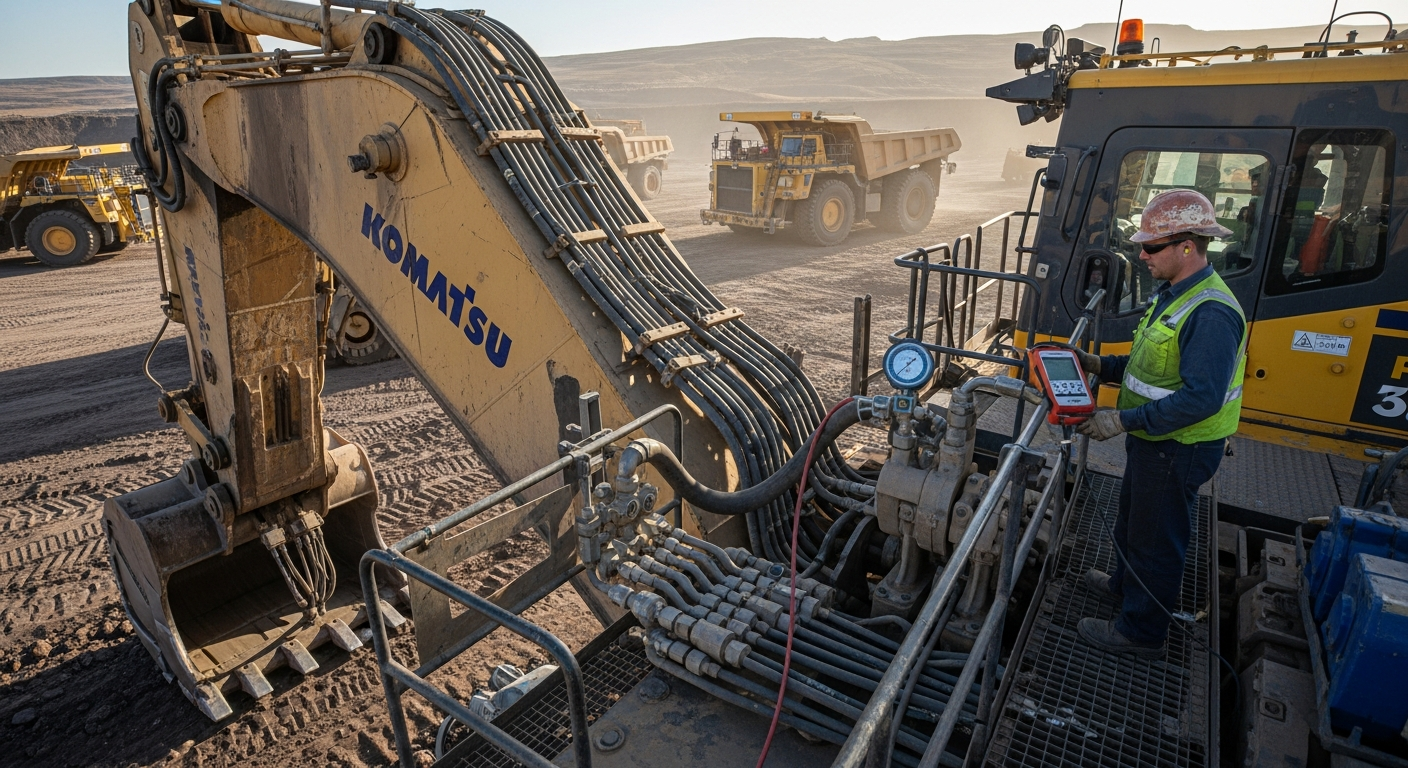
Hydraulic cylinders are essential components in the realm of modern engineering, serving as powerful fluid power actuators that translate hydraulic energy into linear mechanical force. This conversion process is vital for the operation of countless industrial machinery and equipment, facilitating tasks that require significant power and controlled motion. They are characterized by their ability to generate immense force from relatively small inputs, making them a cornerstone of many systems where efficient energy transfer is paramount.
What are Fluid Power Actuators?
Fluid power actuators, such as hydraulic cylinders, are devices that convert energy stored in a pressurized fluid into mechanical motion. In hydraulic systems, an incompressible fluid, typically oil, is pressurized by a pump. This pressurized fluid is then directed to the cylinder, where it pushes against a piston, causing it to move linearly. This linear movement can be used to push, pull, lift, or clamp objects, making these components incredibly versatile. The principle behind their operation involves Pascal’s Law, which states that pressure applied to an enclosed fluid is transmitted undiminished to every portion of the fluid and the walls of the containing vessel.
Industrial Machinery and Motion Control
In industrial machinery, hydraulic cylinders play a crucial role in motion control. They are found in presses, excavators, forklifts, and injection molding machines, where their ability to provide smooth, controlled, and powerful movement is indispensable. The precise control offered by hydraulic systems allows operators to execute complex tasks with accuracy, improving both safety and efficiency in various manufacturing and construction environments. This robust design ensures reliability even under extreme loads and harsh operating conditions.
Engineering Components in Automation Systems
As key engineering components, hydraulic cylinders are integral to automation systems. They contribute to the efficiency and functionality of automated processes by providing reliable linear actuation. In automated assembly lines, for instance, they can be used for clamping workpieces, positioning tools, or ejecting finished products. The integration of these components into complex systems requires careful design and selection to ensure compatibility and optimal performance, especially when aiming for high levels of precision and repeatability.
Generating Linear Force and Precision
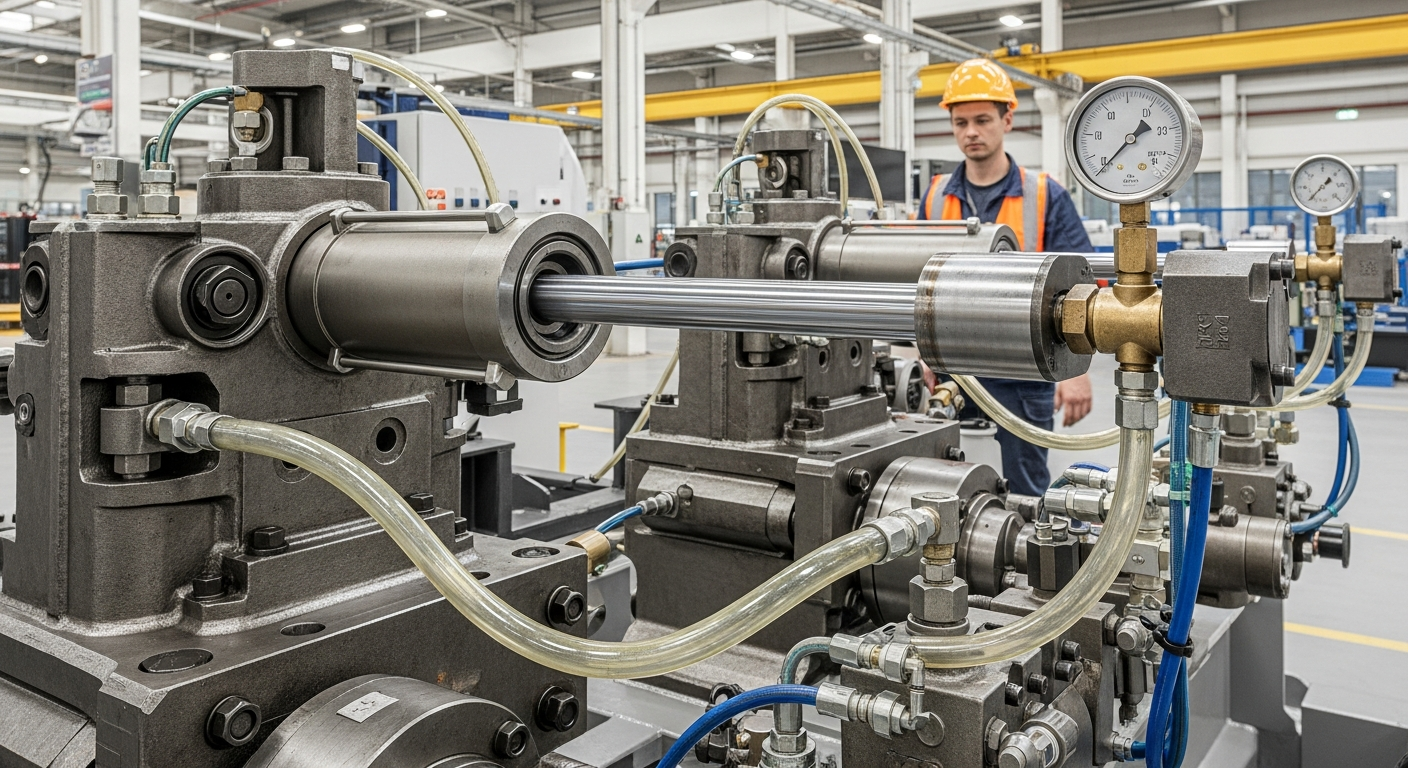
One of the primary advantages of hydraulic cylinders is their capacity to generate substantial linear force. This force is directly proportional to the hydraulic pressure and the surface area of the piston. This characteristic makes them ideal for heavy-duty applications where large forces are required, such as lifting heavy loads or crushing materials. Furthermore, modern hydraulic systems can achieve remarkable precision in their motion control, thanks to advanced valve mechanisms and feedback systems, allowing for very fine adjustments and accurate positioning.
Design and Manufacturing Mechanisms
The design and manufacturing mechanisms of hydraulic cylinders are critical for their performance and longevity. Cylinders are typically constructed from high-strength steel to withstand the immense pressures involved. Key components include the cylinder barrel, piston, rod, and seals. The quality of these components and the precision of their assembly directly impact the cylinder’s efficiency, leak resistance, and lifespan. Continuous advancements in materials science and manufacturing techniques contribute to more durable and efficient hydraulic cylinders, enhancing their role in diverse equipment and systems globally.
Hydraulic cylinders come in various types and sizes, influencing their cost estimation. Factors such as bore size, stroke length, operating pressure, material, and specialized features (e.g., cushioning, position sensing) all contribute to the final price. While specific provider pricing varies significantly, a general overview of typical cost ranges can be useful for planning purposes.
| Type of Cylinder | Application | Estimated Cost Range (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Small Bore, Single-Acting | Light industrial, agricultural | 100 - 500 |
| Medium Bore, Double-Acting | Construction, material handling | 500 - 2,500 |
| Large Bore, Heavy Duty | Mining, marine, specialized industrial | 2,500 - 15,000+ |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
In conclusion, hydraulic cylinders are indispensable mechanical energy conversion devices that underpin a vast array of industrial and automation applications. Their ability to deliver high linear force with precision control by converting fluid power makes them critical components in machinery and systems across various sectors. From heavy equipment to intricate manufacturing mechanisms, their robust design and efficient operation continue to drive progress and innovation in engineering worldwide.