Linear Actuators in Modern Engineering Designs
Linear actuators are fundamental components in a vast array of modern engineering designs, playing a critical role in converting various forms of energy into linear motion. These devices are essential for precise control and movement across numerous industrial applications, from manufacturing machinery to heavy construction equipment. Understanding their operational principles and diverse types, particularly hydraulic cylinders, is key to appreciating their widespread impact on automation, efficiency, and force application in contemporary technology.
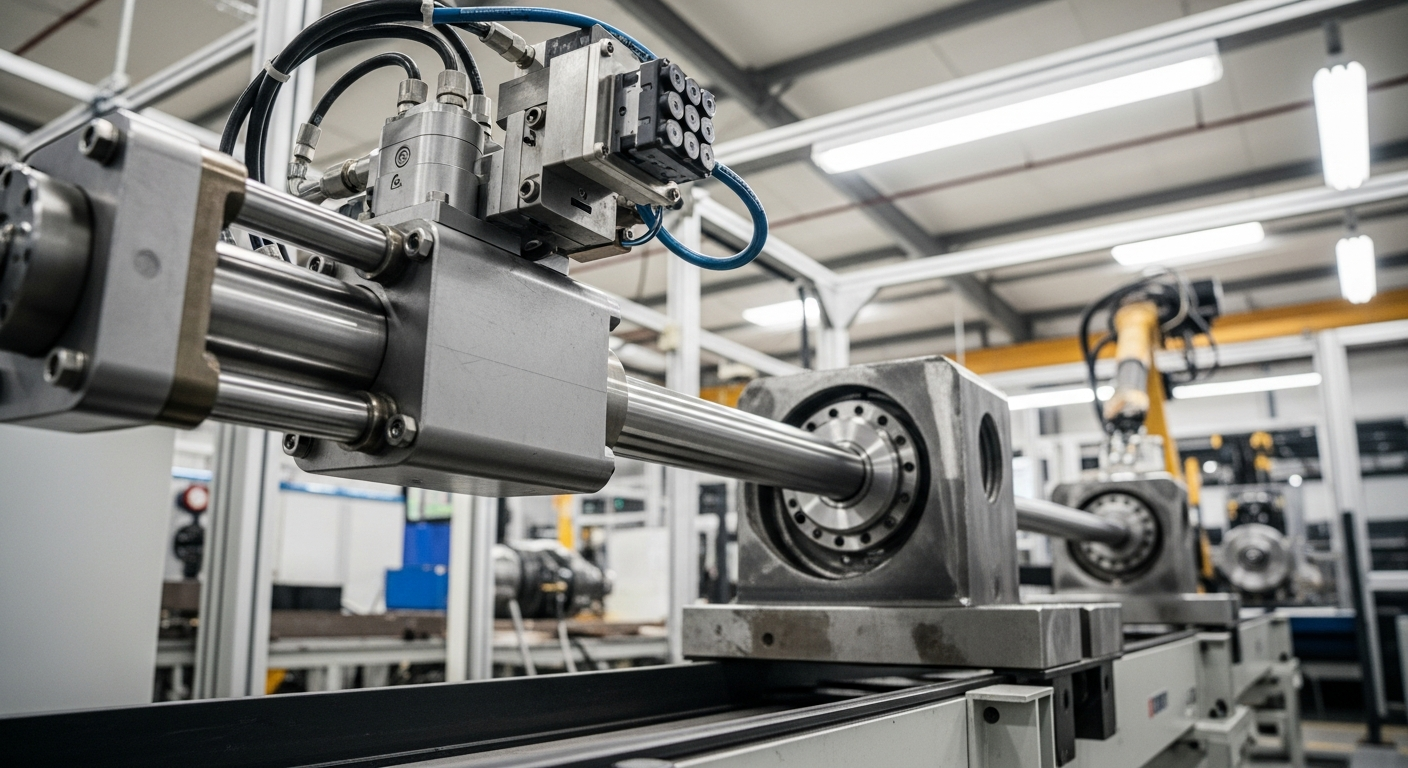
Linear actuators are indispensable components in the realm of modern engineering, facilitating the controlled application of linear motion across countless applications. They are designed to convert energy, whether electrical, pneumatic, or hydraulic, into a straight-line pushing or pulling force, enabling machinery to perform specific tasks with precision. This fundamental capability makes them central to the functionality of complex systems in various industrial sectors, contributing significantly to advancements in automation and mechanical operations.
Understanding Linear Actuation Principles
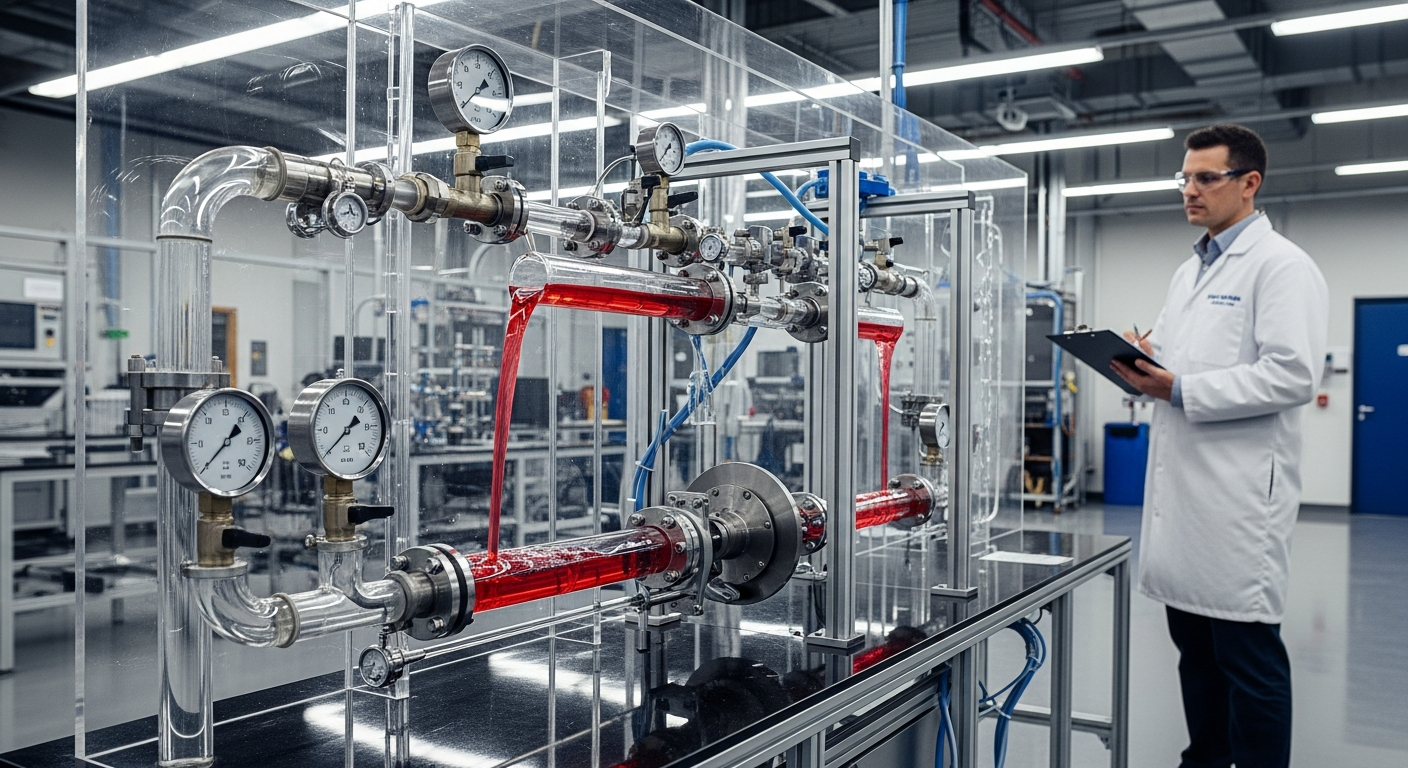
At its core, linear actuation involves the transformation of rotational or fluid power into a straight-line movement. This mechanical process is crucial for tasks requiring components to move back and forth, up and down, or in and out. The principle relies on a drive system that translates the input energy into a controlled displacement. Different types of linear actuators utilize various mechanisms, but the objective remains consistent: to provide a reliable and often high-force solution for specific movement requirements within an engineering design. The careful control of this motion is vital for the safety and efficiency of the equipment.
Hydraulic Cylinders: A Key Fluid Power Component
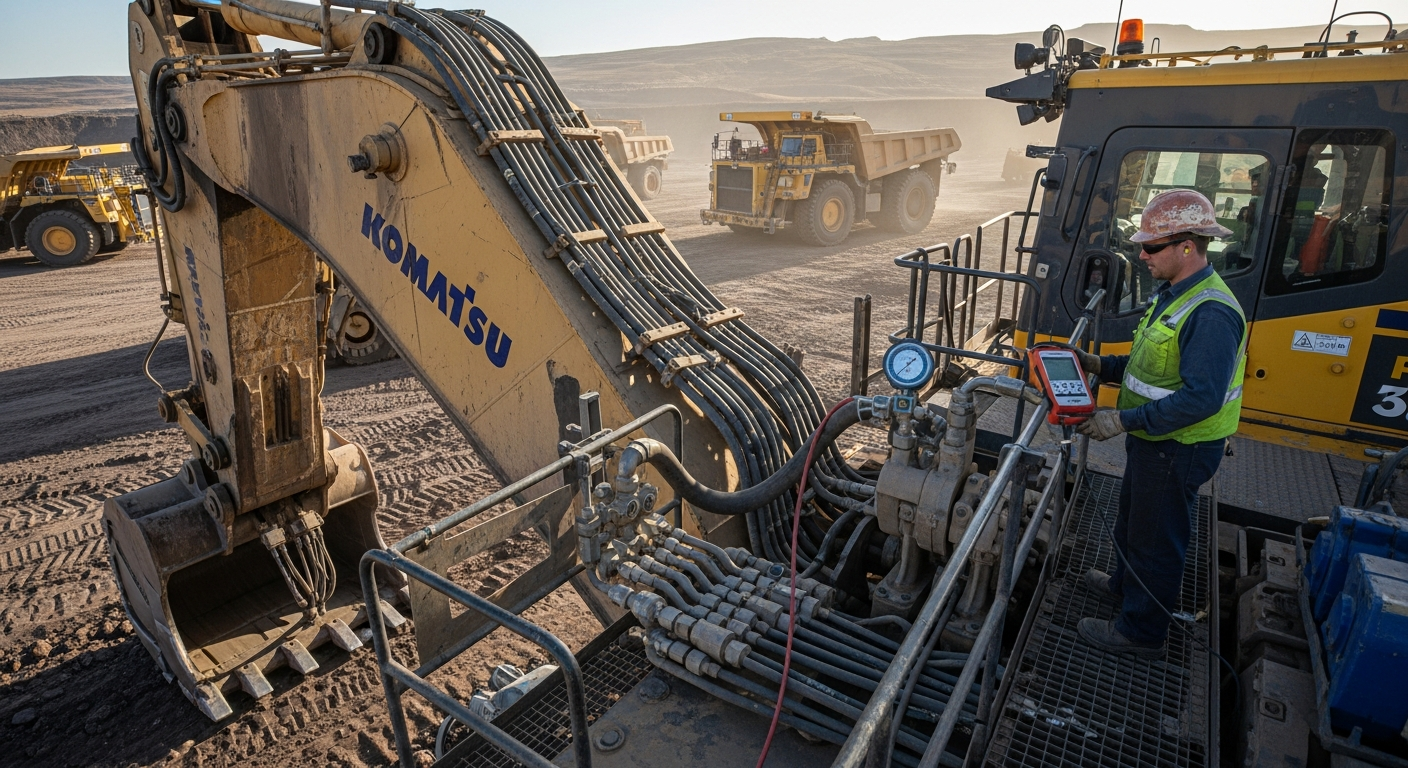
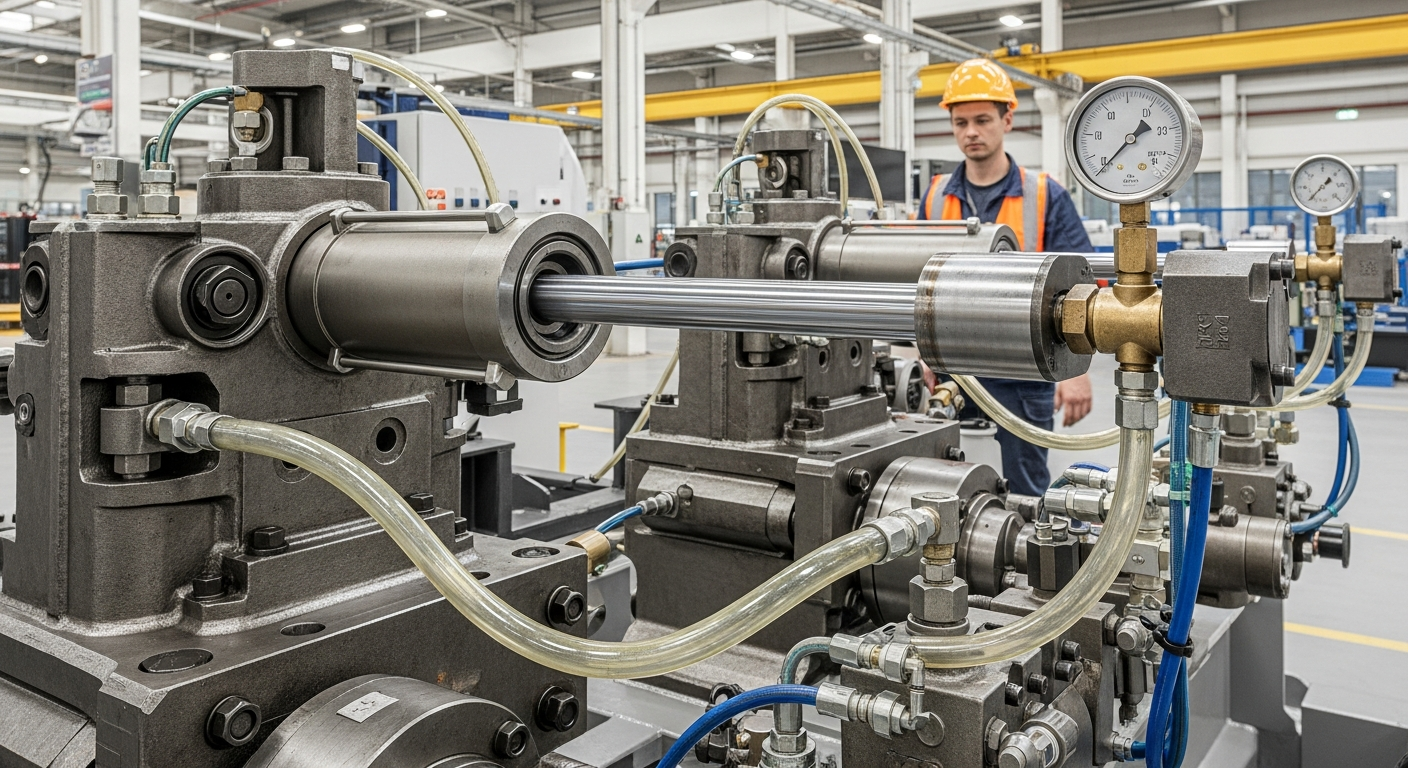
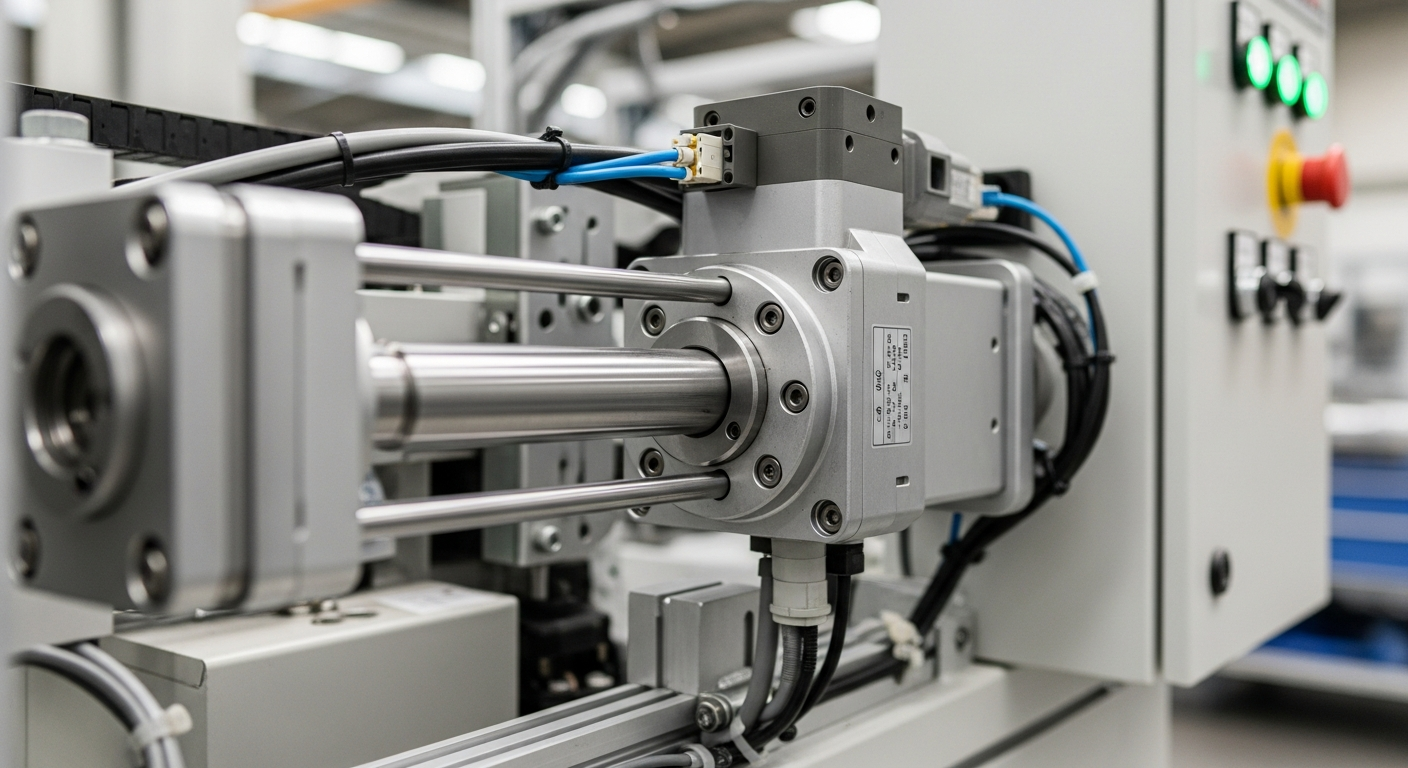
Hydraulic cylinders are a prominent example of linear actuators, operating on the principle of fluid power. They consist of a cylinder barrel, a piston connected to a piston rod, and a port for hydraulic fluid. When pressurized hydraulic fluid is introduced into the cylinder, it exerts force on the piston, causing it to move linearly. This system can generate immense force, making hydraulic cylinders ideal for heavy-duty applications. Their robust design and ability to handle high pressures make them essential components in situations demanding significant mechanical power and precise control over movement.
Applications in Industrial and Heavy Equipment
The versatility of hydraulic cylinders extends across a broad spectrum of industrial and heavy equipment. In manufacturing, they are integral to presses, clamping mechanisms, and material handling systems, ensuring efficient process flow. For construction and mining, hydraulic cylinders are the workhorses of excavators, bulldozers, and cranes, enabling lifting, digging, and other strenuous tasks. Their ability to deliver consistent force and controlled movement is critical for the reliable operation of such machinery, underpinning the productivity and safety of these sectors through advanced engineering technology.
Precision and Efficiency in Automation Processes
Modern automation relies heavily on the precision and efficiency offered by linear actuators, including hydraulic systems. In automated production lines, these components provide the accurate positioning and controlled movement necessary for repetitive tasks, reducing human error and increasing output. The ability to precisely control the speed and force of a hydraulic cylinder means that complex processes can be executed with high repeatability. This level of control is paramount in industries where tight tolerances and consistent performance are required, driving overall system efficiency and technological advancement.
Selecting Actuators for Engineering Designs
Selecting the appropriate linear actuator for an engineering design involves considering several factors, including the required force, stroke length, speed, and environmental conditions. Engineers must evaluate the specific needs of the application, such as the level of precision, the duty cycle, and the available power source. Integrating these components effectively into a larger system demands a thorough understanding of their capabilities and limitations. Proper selection and system design ensure optimal performance, longevity, and cost-effectiveness for the overall equipment and process.
Linear actuators, particularly hydraulic cylinders, are foundational elements in contemporary engineering, offering robust solutions for converting energy into controlled linear motion. Their indispensable role in generating significant force, enabling precision, and driving automation underscores their importance across various industrial sectors. As technology continues to evolve, the principles and applications of these mechanical components will remain central to the development of more efficient, powerful, and automated systems worldwide.